The European Union economy is one of the world's largest integrated markets, built on free movement of goods, services, capital, and labor. Advanced manufacturing, high-value services, and strong export capacity define its economic structure, with Germany, France, Italy, and the Netherlands playing major roles. The EU benefits from deep supply-chain integration and strong regulatory standards, supporting competitiveness in automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and green technologies. Challenges include demographic aging, varied fiscal positions among members, and the energy transition, yet substantial investment in digital infrastructure, sustainability, and innovation continues to strengthen long-term economic resilience and productivity.
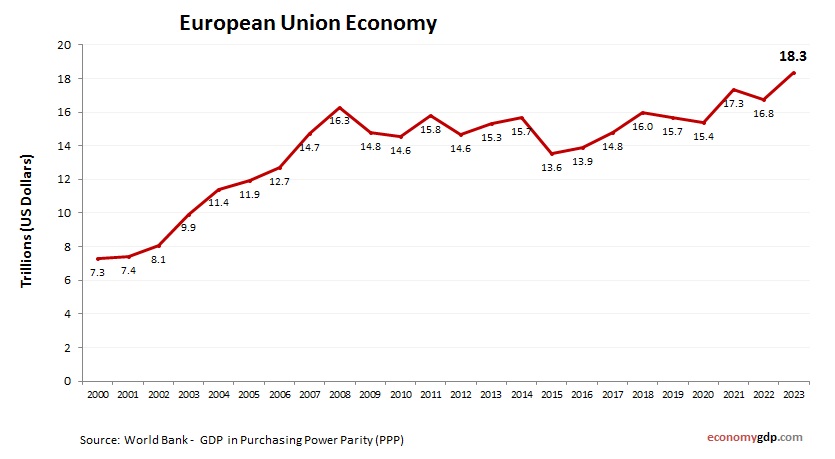
World Bank Data. 2000-2024. Last updated Oct 2025. Refer to the latest year-over-year European Union GDP statistics.
