The European Union economy is a global powerhouse, driven by diverse industries, services, and trade. Manufacturing, particularly in Germany and France, includes automobiles and machinery, while services dominate in finance and technology. Agriculture and renewable energy are also key. Integration fosters intra-EU trade, but Brexit, geopolitical tensions, and aging populations pose challenges. Investments in green technology and digitalization aim to maintain competitiveness, though regional disparities and regulatory complexity persist.
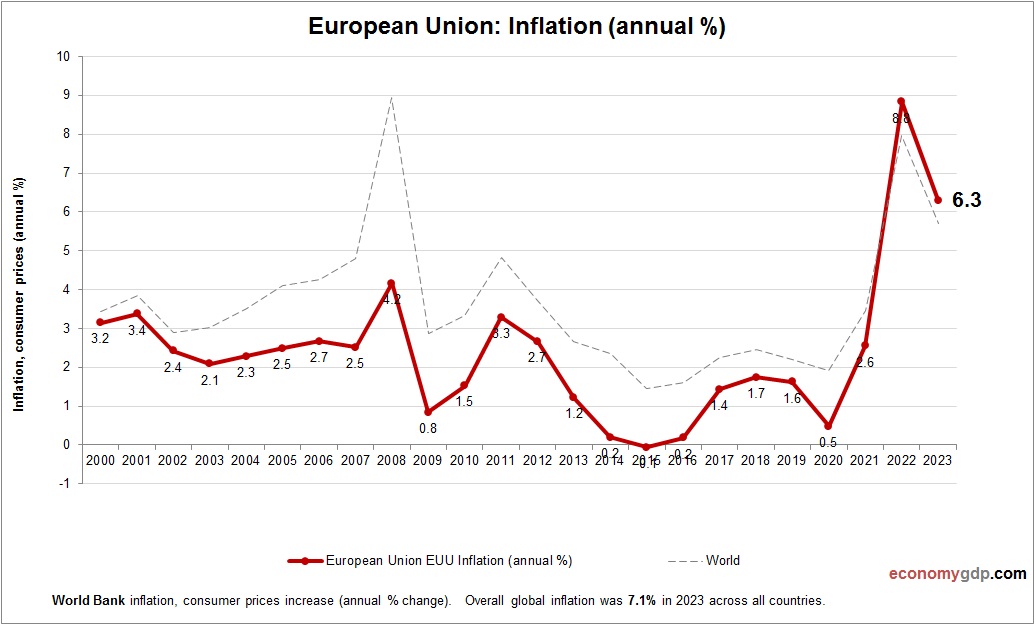
European Union Economy Size
The EU’s economy, valued at $17 trillion, is one of the world’s largest. Industry, services, and trade drive its collective GDP, with significant global influence. See European Union GDP.

European Union Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
The European Union’s economy has a PPP GDP of $25 trillion, exceeding its $17 trillion nominal GDP, reflecting varied local costs across member states. PPP per capita averages $50,000, ranging from $30,000 in Bulgaria to $140,000 in Luxembourg. PPP underscores the EU’s massive domestic market, driven by industry and services, with trade amplifying its global influence.

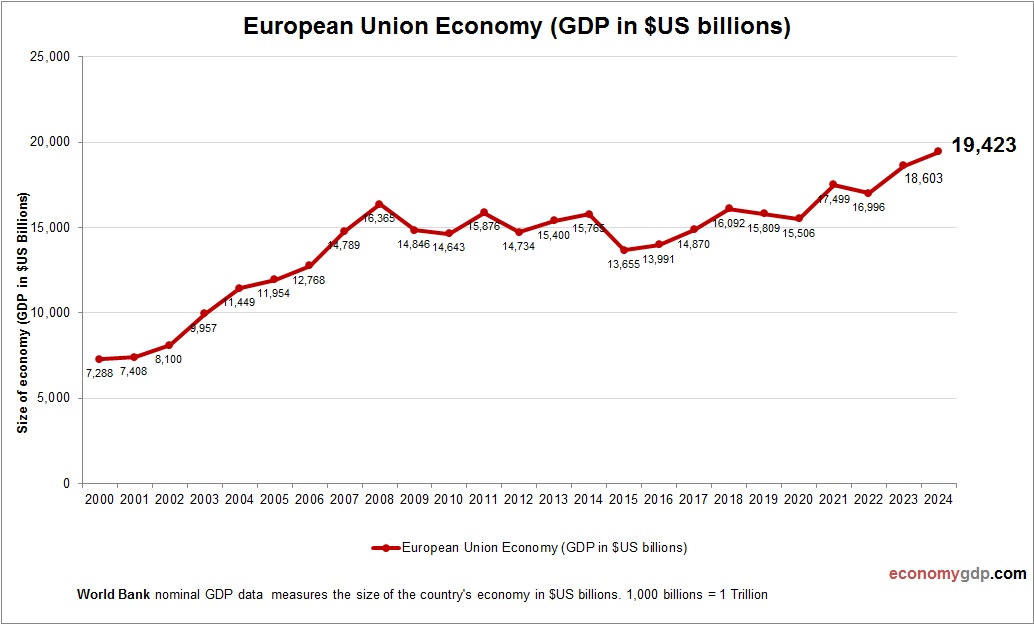
European Union Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 2.0% in 2024, driven by EU trade and services. Industry and agriculture support growth, but high debt and energy import reliance limit gains. Infrastructure investments and regional integration drive resilience, while innovation and green energy contribute to stability, positioning the economy for moderate expansion.
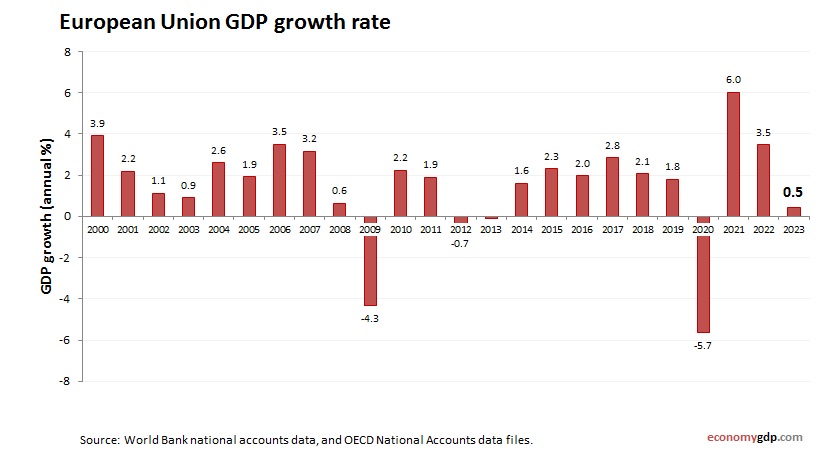
European Union Inflation
The European Union’s inflation rate averages 2.5% in 2024, driven by rising energy and food prices across member states. Supply chain disruptions and wage growth add pressure, while strong exports in countries like Germany sustain demand. Eurozone monetary tightening and fiscal coordination help stabilize, though import reliance keeps inflation moderate.