Indonesia’s economy relies on agriculture, mining, and manufacturing. Palm oil, rubber, and coffee dominate agricultural exports, while coal and nickel mining are significant. Manufacturing includes textiles and electronics. Emerging industries include digital economy, with e-commerce giants like Tokopedia, and green energy, particularly geothermal and solar. Indonesia’s young population and growing middle class drive consumption. Infrastructure development, like the new capital Nusantara, supports growth, though logistical challenges persist. Its focus on sustainable resource management and tech startups positions Indonesia as a rising economic power in Southeast Asia, with strong regional trade ties.
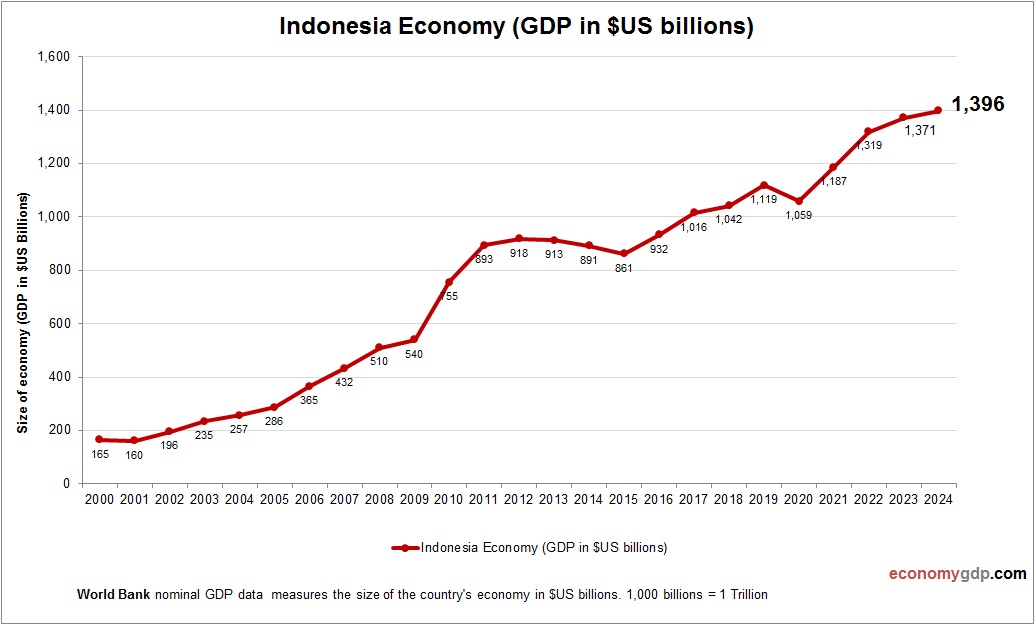
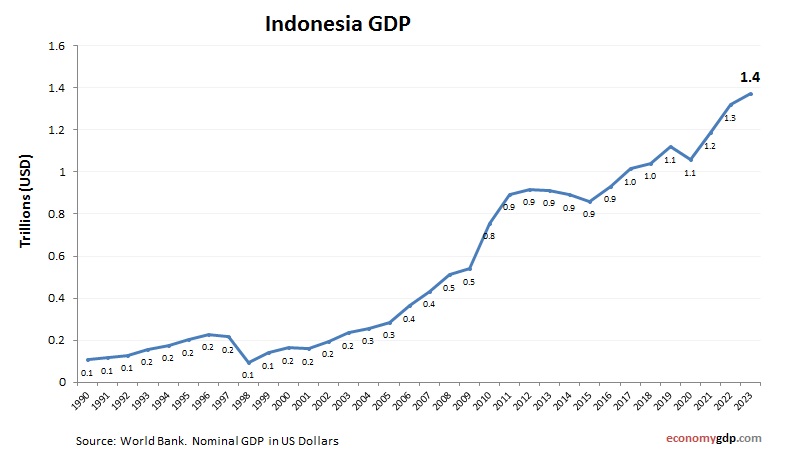
Indonesia Economy Size
Indonesia’s economy, with a nominal GDP of about $1.2 trillion, is Southeast Asia’s largest. Agriculture, mining, and manufacturing drive its size, with palm oil and coal as key exports. Its growing consumer market and digital economy bolster GDP. Investments in infrastructure and green energy enhance its economic scale, positioning Indonesia as an emerging regional powerhouse with significant growth potential in ASEAN trade networks. See Indonesia GDP.
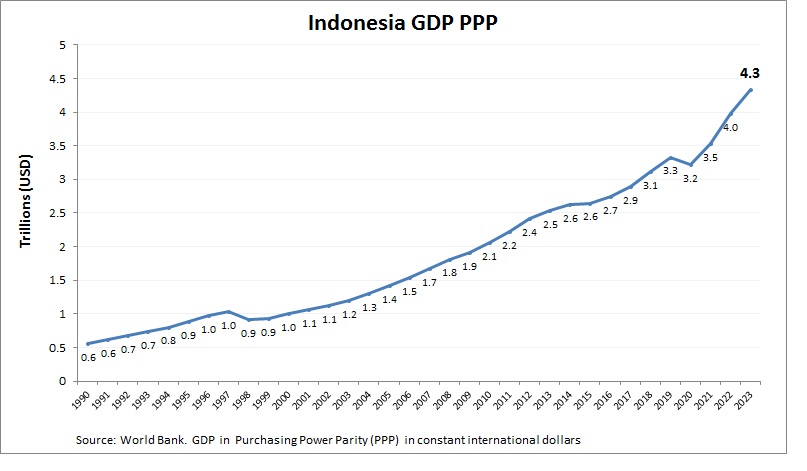
Indonesia Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Indonesia’s economy has a PPP GDP of around $4.4 trillion, reflecting its large population and low costs. Agriculture, mining, and manufacturing drive its size, with palm oil and coal as key exports. Its growing consumer market boosts purchasing power, enhancing its PPP GDP. Investments in digital economy and green energy support its scale, positioning Indonesia as a major ASEAN economy with significant growth potential.
Indonesia Growth Rate
Indonesia’s economy is projected to grow at 4.7% in 2025. Agriculture, mining, and manufacturing drive expansion, with palm oil and nickel exports boosting growth. A young population and digital economy, including e-commerce, fuel momentum. Infrastructure development, like the new capital Nusantara, supports progress, though logistical challenges persist. Indonesia’s strong growth positions it as a leading ASEAN economy with significant regional influence.

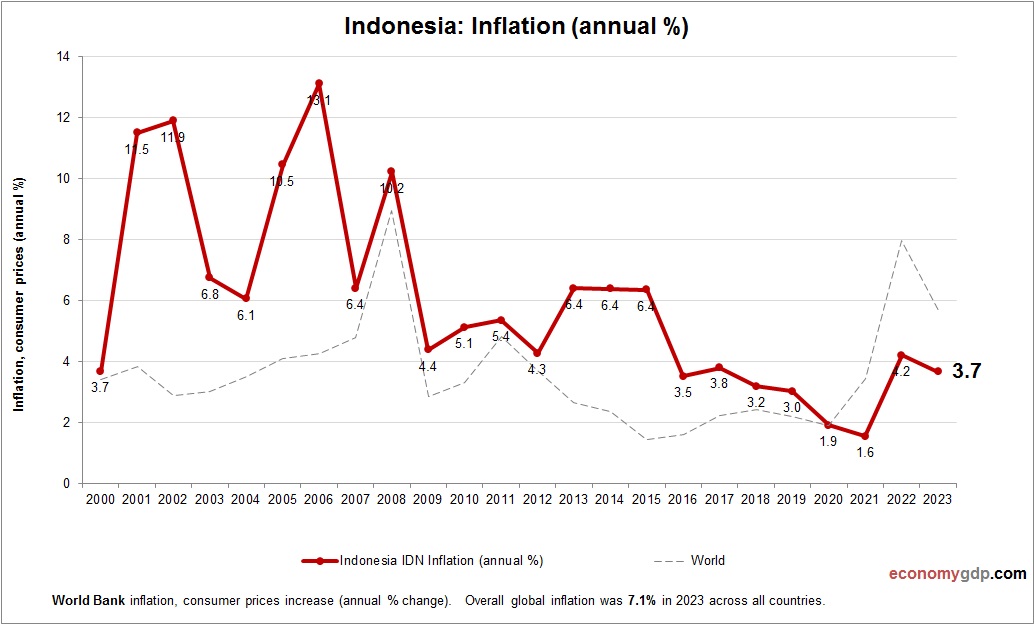
Indonesia Inflation
The Indonesia’s inflation is moderate at 3%, driven by food and fuel price fluctuations. Strong domestic demand and palm oil exports add pressure, but government subsidies and stable commodity markets curb inflation. Infrastructure projects and digital economy growth contribute modestly, while a young consumer base sustains price increases. Monetary policy keeps inflation in check, supporting robust economic growth.