The Ethiopia economy is one of Africas fastest-growing, driven by agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Coffee is a major export, while textiles and leather goods gain traction. Large-scale infrastructure projects, like the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, boost energy and trade. However, political instability, debt, and drought risks hinder progress. Foreign investment, particularly from China, supports growth, with efforts to industrialize and improve education aiming for long-term development.
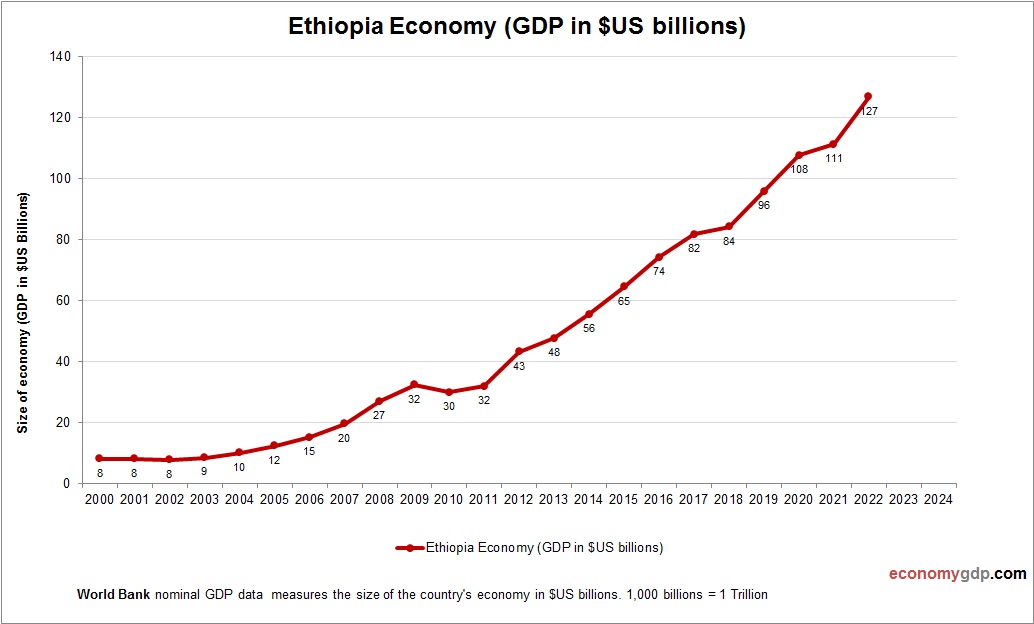
Ethiopia Economy Size
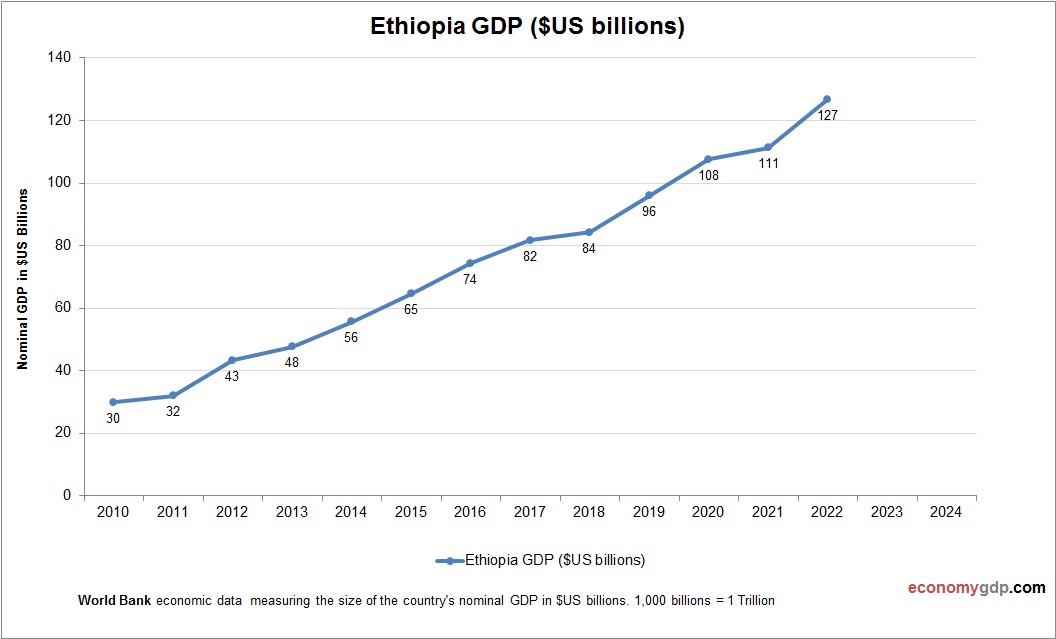
Ethiopia’s economy, at $120 billion, is large for East Africa, driven by agriculture and industry. Rapid growth has expanded its GDP, though poverty persists. See Ethiopia GDP.
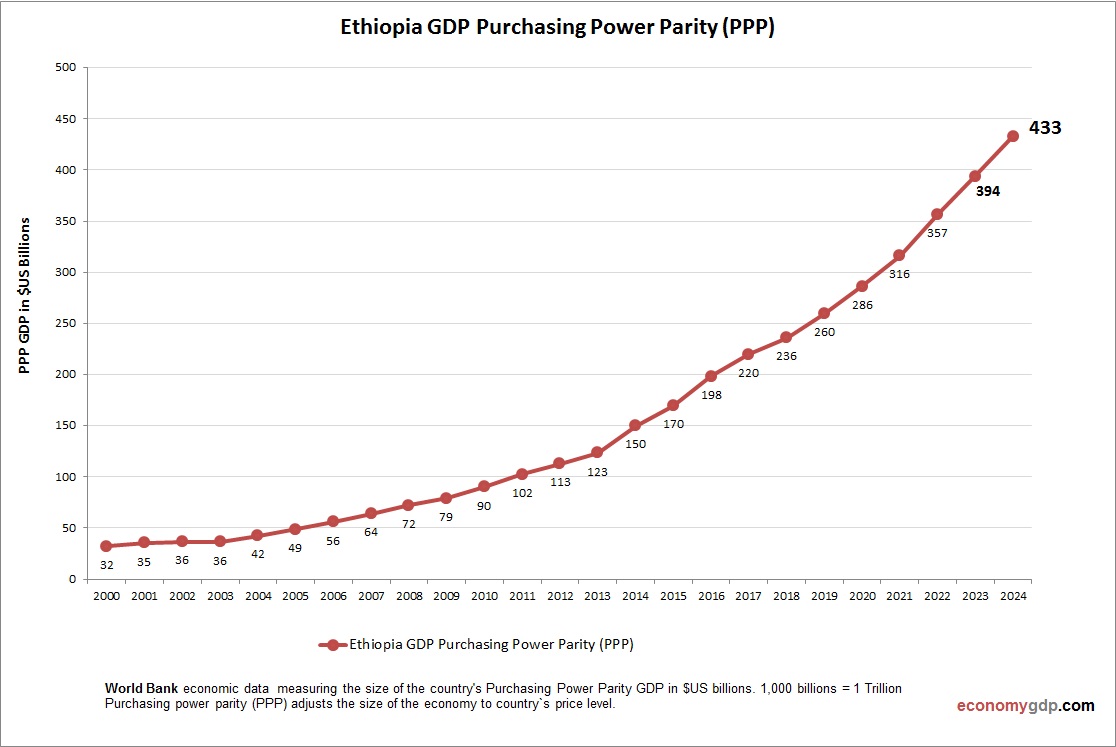
Ethiopia Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Ethiopia’s economy has a PPP GDP of $400 billion, over three times its $120 billion nominal GDP, driven by low costs for agriculture and industry. PPP per capita is around $3,500, indicating low purchasing power. Rapid growth boosts domestic markets, but poverty and infrastructure gaps limit broader PPP benefits.
Ethiopia Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 6.8% in 2024, driven by agriculture and manufacturing. Coffee and textile exports support growth, but infrastructure deficits and political tensions pose risks. Foreign investment and a young workforce drive resilience, while regional trade integration enhances momentum, positioning the economy as a regional growth leader.

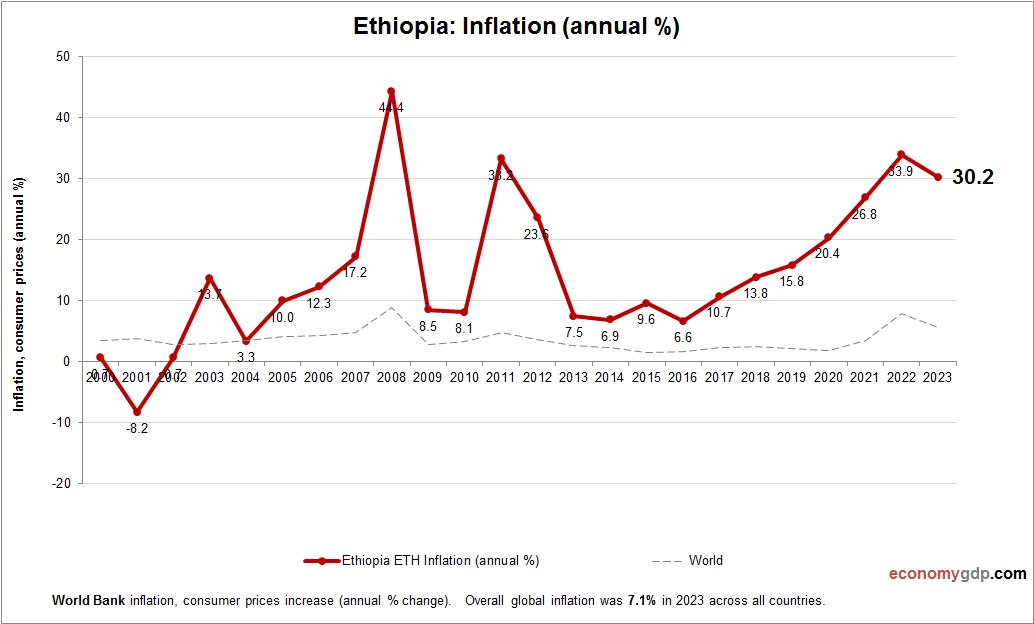
Ethiopia Inflation
Ethiopia’s inflation rate is about 20% in 2024, driven by currency depreciation and conflict-related supply disruptions. Rising global food and fuel prices increase import costs, while agricultural setbacks from drought add pressure. Fiscal expansion fuels demand, with limited monetary tools sustaining high inflation in this fast-growing but challenged economy.