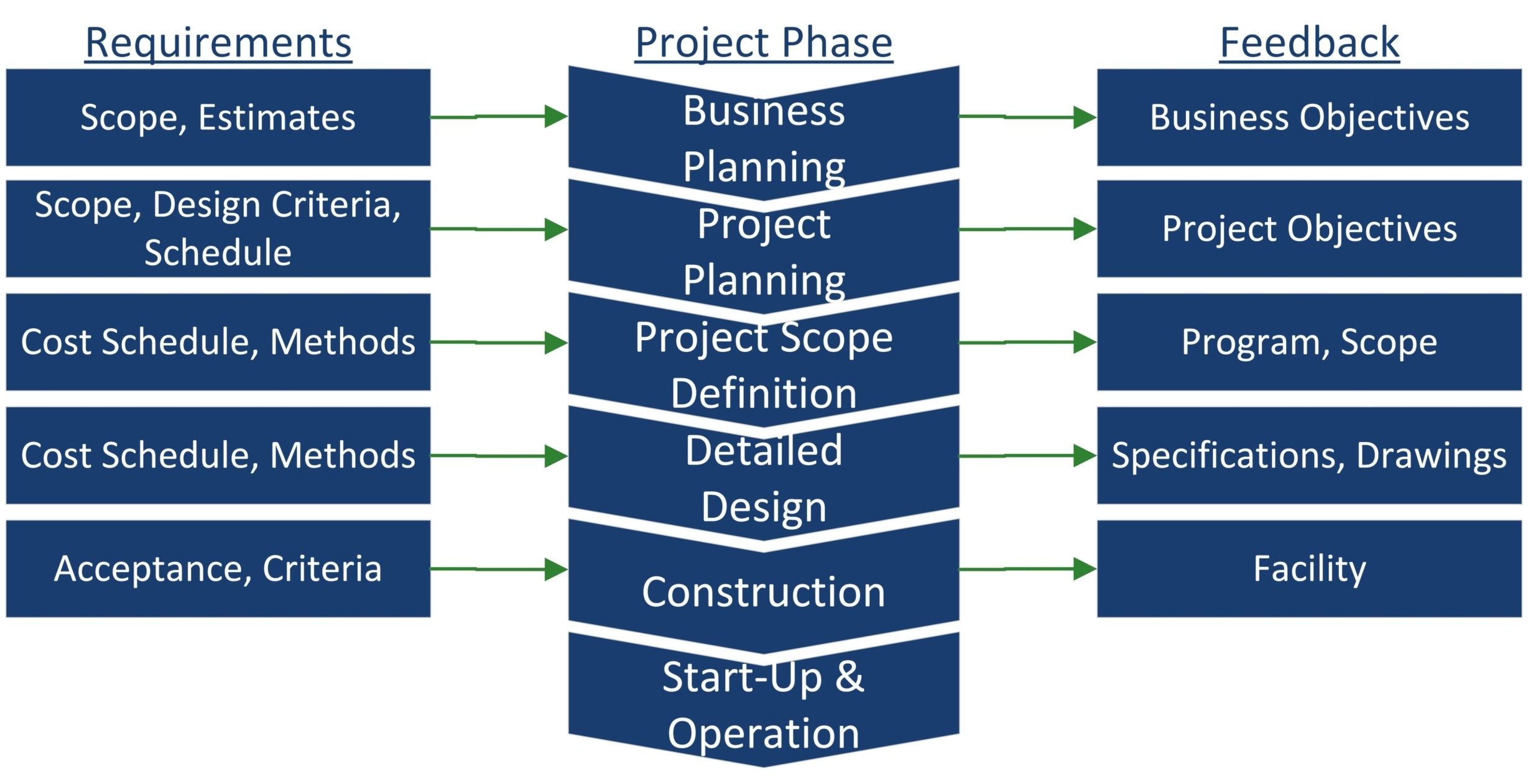
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) organizes project phases according to their life cycle, starting with Project Initiation and ending in Project Closure. The five phases of project management are:
1. Project Initiation: This phase is where the project idea is defined, and the project sponsor evaluates it and authorizes the project to proceed. The main goal of this phase is to ensure that the project meets business needs and that stakeholders and project teams are aligned on the project success criteria throughout the project life cycle .
2. Project Planning: This phase involves defining the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. The project manager creates a detailed project plan that outlines the tasks, timelines, resources, and budget required to complete the project successfully .
3. Project Execution: This phase involves executing the plan created in the previous phase. The project team performs the tasks outlined in the plan, and the project manager monitors progress to ensure that everything is on track .
4. Project Monitoring & Control: This phase involves monitoring and controlling the progress of the project to ensure that it stays on track. The project manager tracks progress against the plan, identifies any deviations from the plan, and takes corrective action as necessary .
5. Project Closure: This phase involves closing out the project once all objectives have been met. The project manager ensures that all deliverables have been completed, all stakeholders have been satisfied, and all resources have been released .
Each phase of the project management life cycle consists of a specific project objective or objectives and defines results, deliverables, processes, and milestones. Management by project life cycle phase gives the project team a common vocabulary to communicate project progress, resulting in better organizational control over the projects they handle.
