Nigeria’s economy, Africa’s largest at $440 billion, is driven by oil, which accounts for 80% of export revenues. Agriculture employs 35% of the workforce, producing cassava, yams, and cocoa. The tech sector, centered in Lagos, is booming, with fintech startups like Flutterwave leading innovation. Manufacturing, including cement and textiles, and entertainment (Nollywood) are growing. Diversification efforts focus on renewables and mining. Despite potential, corruption, infrastructure deficits, and insecurity hinder growth. Nigeria’s young population and digital economy offer opportunities for future expansion.
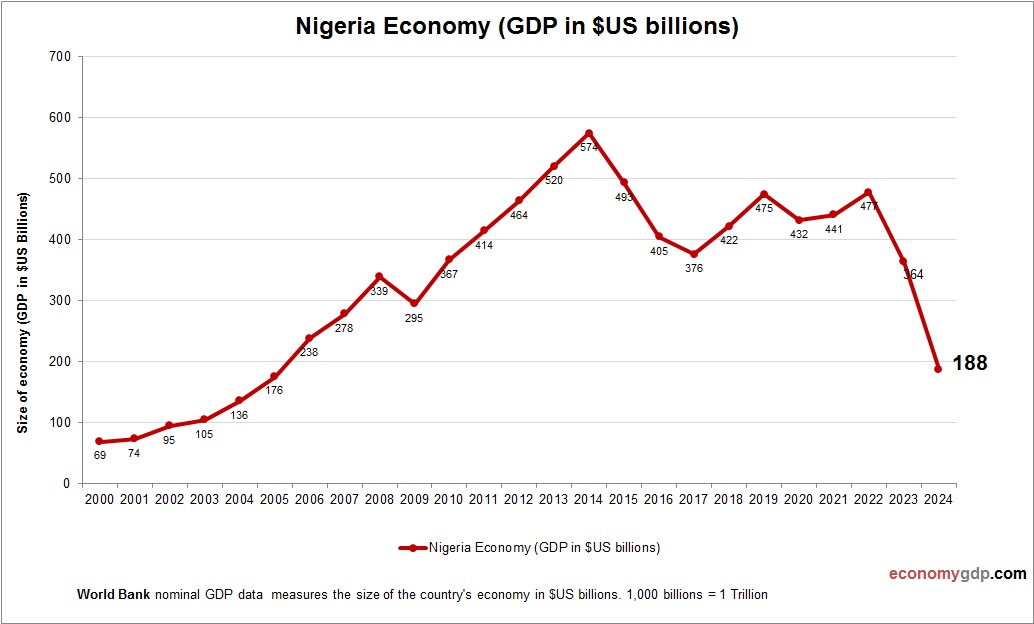
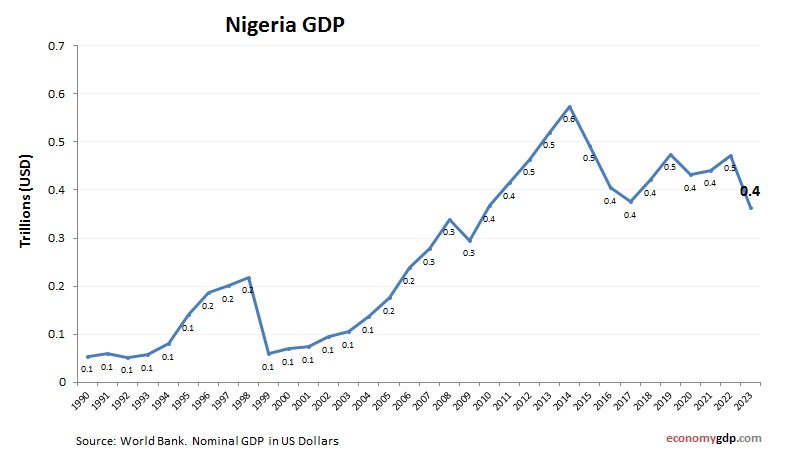
Nigeria Economy Size
Nigeria’s economy, at $440 billion, is Africa’s largest, with oil and services driving its GDP, despite challenges from corruption and insecurity. See Nigeria GDP.
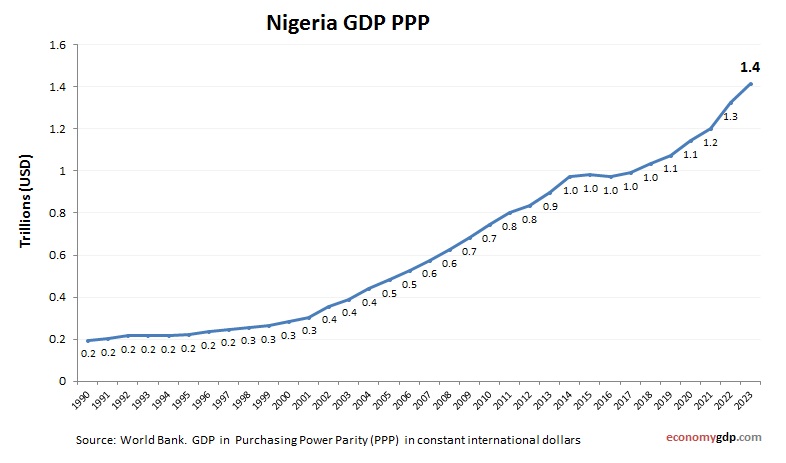
Nigeria Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Nigeria’s economy has a PPP GDP of $1.4 trillion, over three times its $440 billion nominal GDP, due to low costs for oil and services. PPP per capita is around $6,500, indicating modest purchasing power. Domestic pricing boosts markets, but inequality and infrastructure gaps limit broader PPP benefits.
Nigeria Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 5.0% in 2024, propelled by oil exports. High global oil prices and tech growth drive expansion, but corruption and insecurity pose risks. Agriculture and manufacturing contribute, while infrastructure investments drive resilience, positioning the economy as Africa’s largest despite structural challenges.

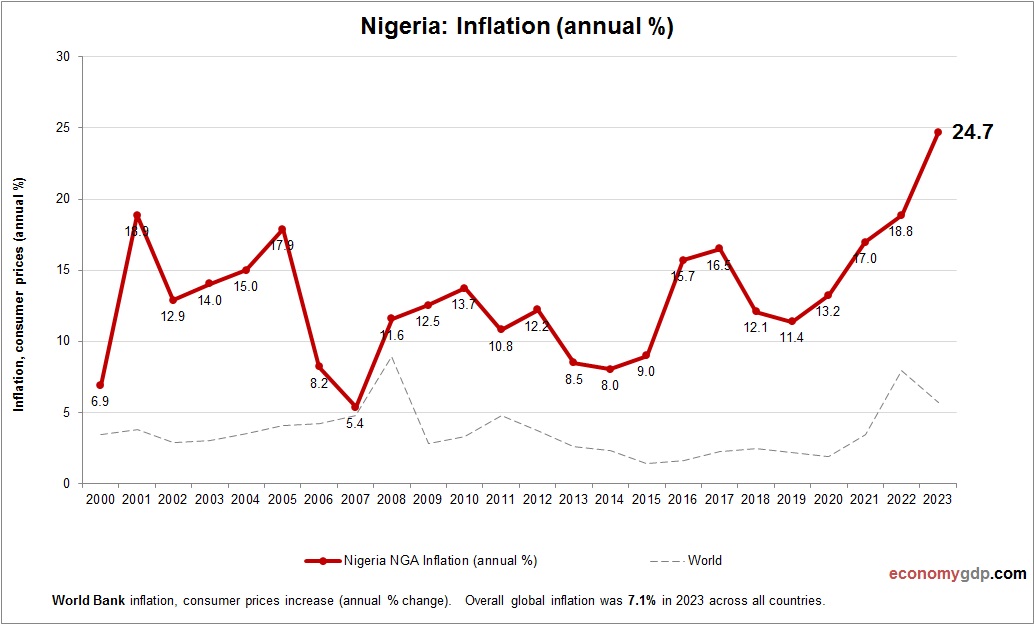
Nigeria Inflation
Nigeria’s inflation rate is about 25% in 2024, driven by currency depreciation and rising global food and fuel prices. Oil export disruptions and agricultural setbacks from flooding increase costs, while fiscal deficits fuel demand. Monetary tightening aims to stabilize, but structural challenges sustain high inflation in this large economy.