Niger’s economy, valued at $15 billion, is dominated by subsistence agriculture, employing 80% of the workforce, with millet, sorghum, and livestock as staples. Uranium mining is a critical export, though declining in global demand. Oil production, started in 2011, is an emerging sector, alongside gold mining. Informal trade and remittances support livelihoods. Solar energy shows potential in this arid nation. Extreme poverty, rapid population growth, and security threats from insurgencies limit development. Investments in infrastructure and education are needed to diversify and stabilize Niger’s economy.
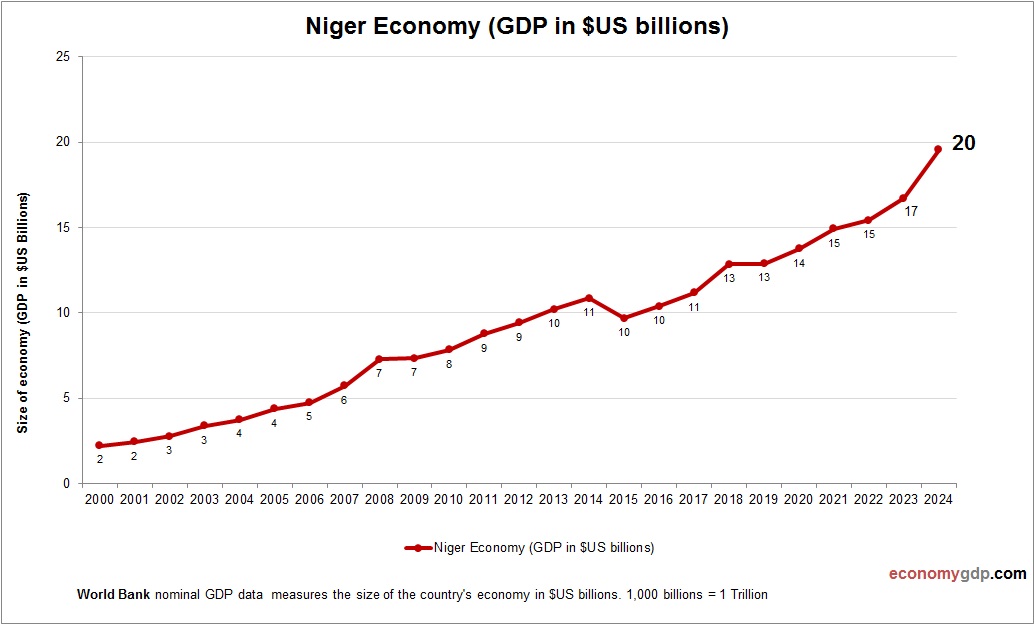
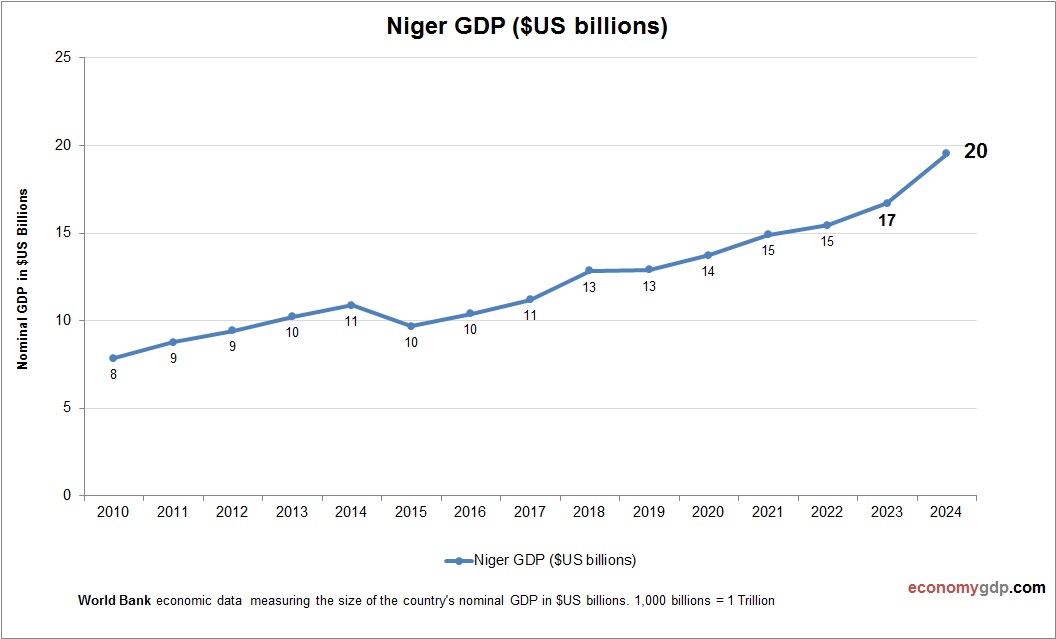
Niger Economy Size
Niger’s economy, worth $15 billion, is small and fragile, with agriculture and uranium driving its GDP, limited by poverty and insecurity. See Niger GDP.
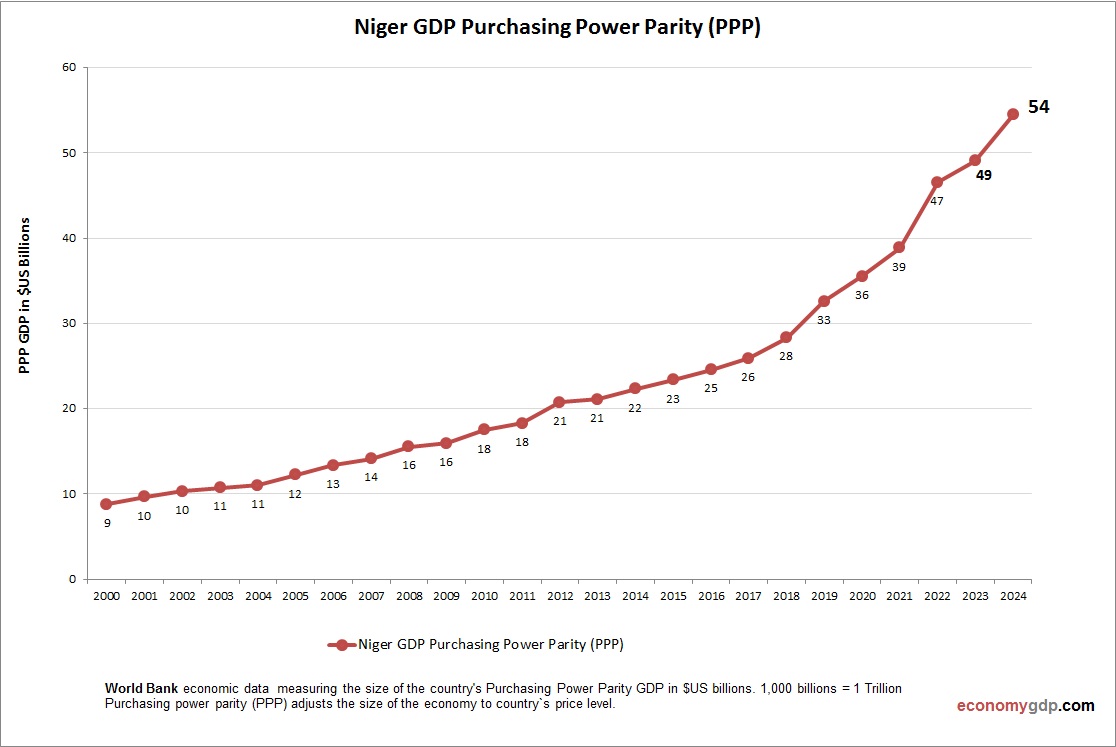
Niger Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Niger’s economy has a PPP GDP of $45 billion, three times its $15 billion nominal GDP, driven by low costs for agriculture and uranium. PPP per capita is around $1,500, among the lowest globally, reflecting extreme poverty. Domestic pricing supports subsistence, but insecurity limits PPP-driven economic growth.
Niger Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 3.5% in 2024, fueled by agriculture and uranium exports. Millet production and foreign investment support growth, but insecurity and poverty pose risks. Regional trade and mining projects drive resilience, while stability enhances momentum, positioning the small economy for steady progress.

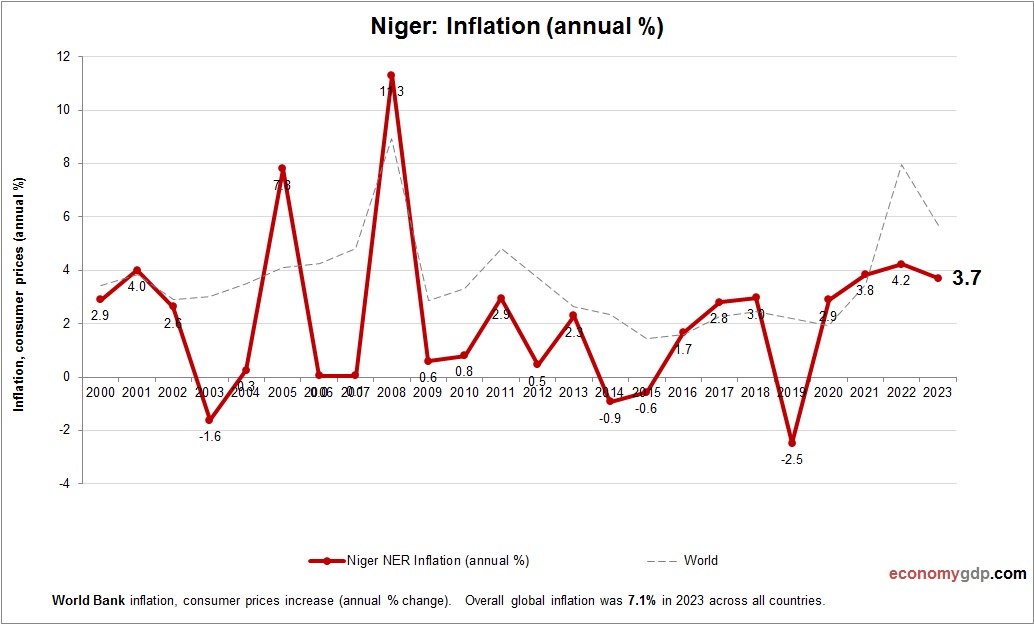
Niger Inflation
Niger’s inflation rate is around 7% in 2024, driven by rising global food and fuel prices in this import-dependent economy. Drought-related agricultural disruptions increase food costs, while currency depreciation adds pressure. Uranium exports fuel demand, but weak infrastructure sustains volatility, with limited policy tools to curb inflation.