The Malta economy is driven by tourism, financial services, and shipping within the EU. Mediterranean attractions and gaming industries draw visitors, while offshore banking benefits from tax advantages. Maritime trade leverages its strategic location. High public debt and reliance on tourism pose risks, with efforts to expand technology and renewable energy underway. EU integration supports growth, though labor shortages and global economic shifts challenge long-term stability.
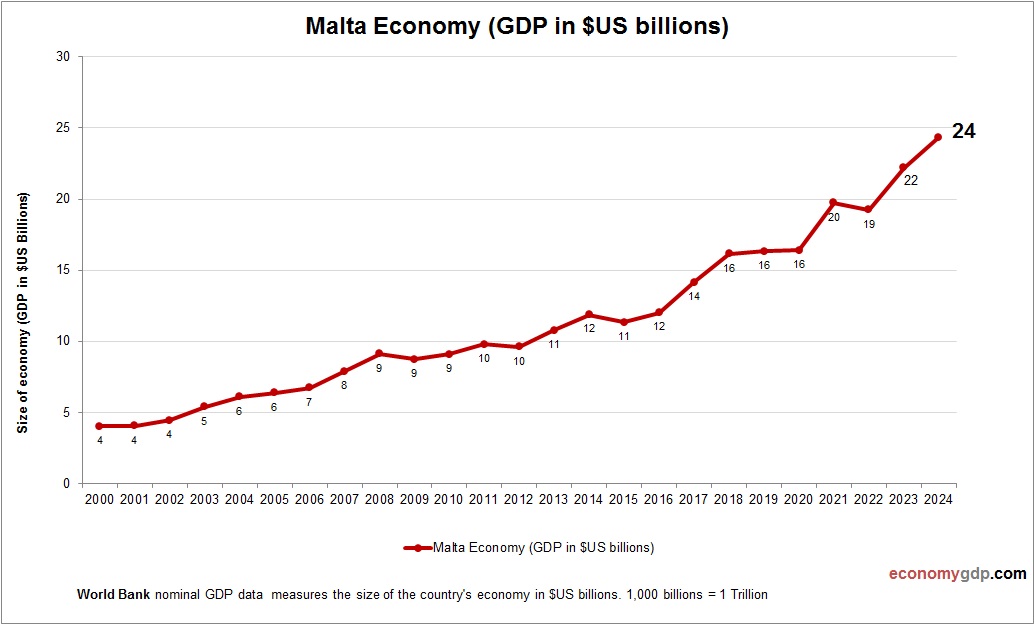
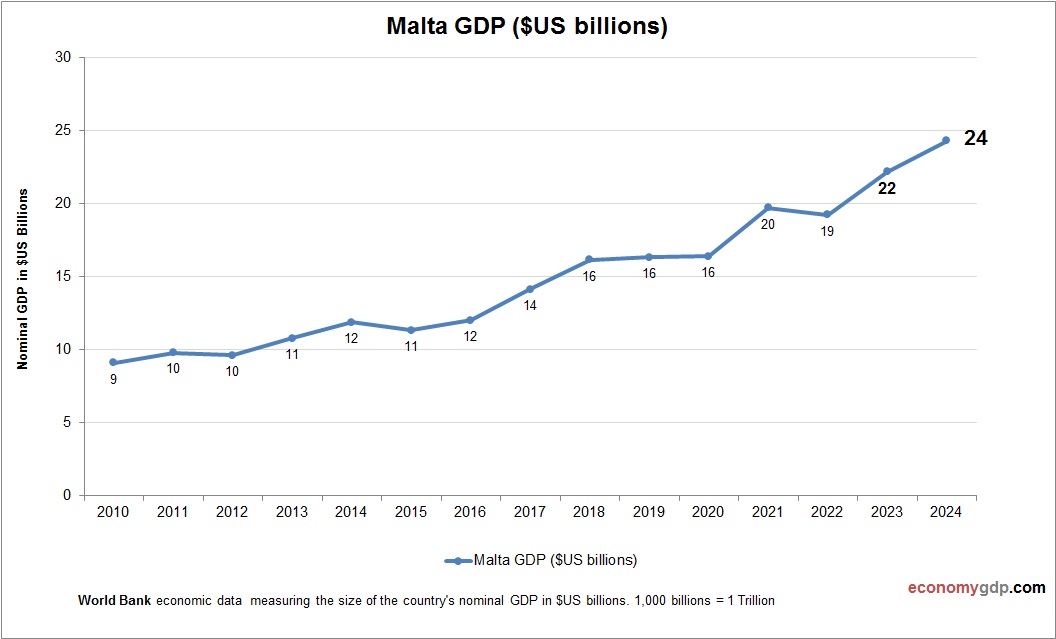
Malta Economy Size
Malta’s economy, worth $15 billion, is small but dynamic, with services and tourism driving its GDP, bolstered by EU membership. See Malta GDP.
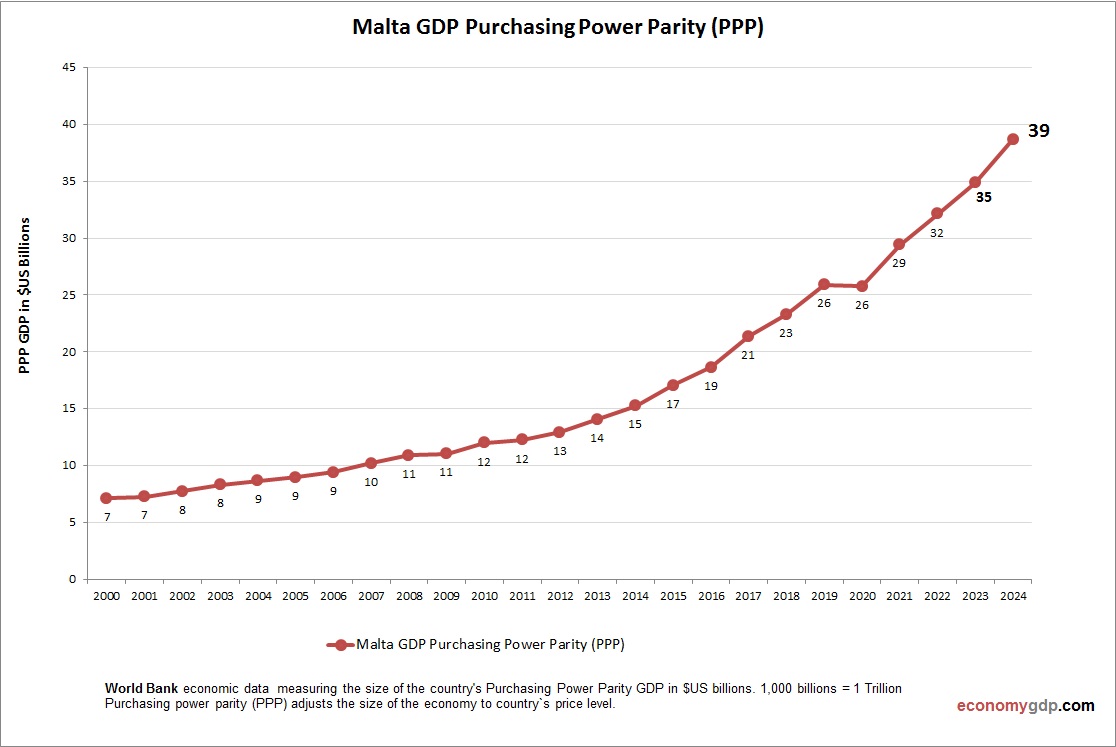
Malta Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Malta’s economy has a PPP GDP of $25 billion, over 1.5 times its $15 billion nominal GDP, reflecting lower costs for services and tourism. PPP per capita is around $50,000, indicating strong purchasing power. Domestic pricing and EU membership amplify markets, supporting robust PPP-driven economic growth.
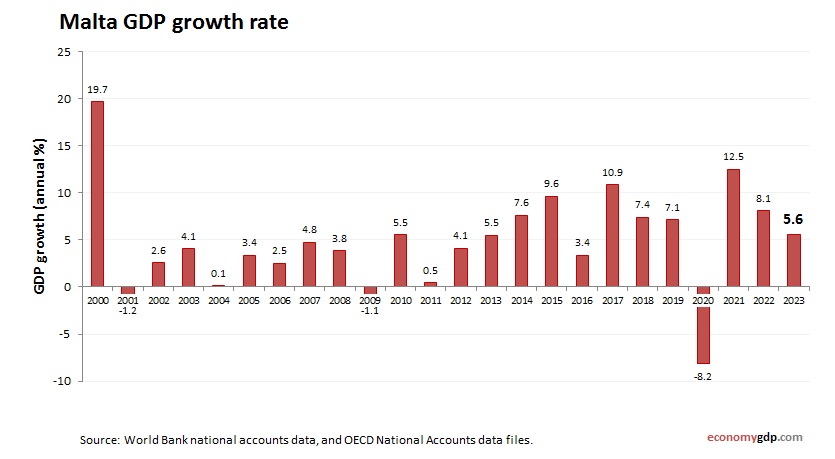
Malta Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 2.5% in 2024, driven by tourism and financial services. EU membership and digital exports support growth, but reliance on services and high costs limit gains. Shipping contributes modestly, while renewable energy drives resilience, positioning the small economy for steady progress.
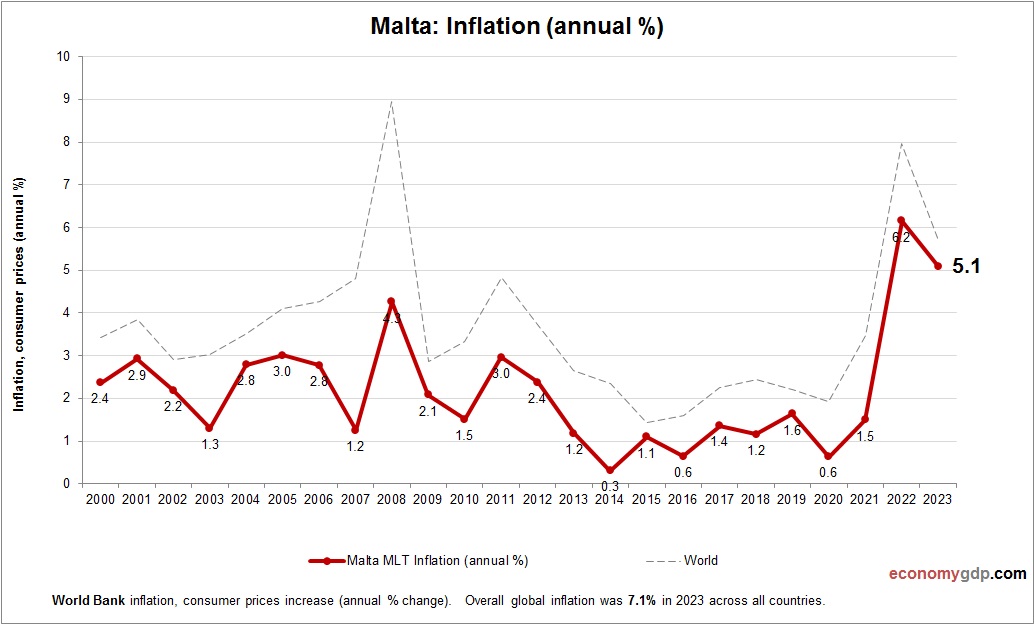
Malta Inflation
Malta’s inflation rate is around 2.5% in 2024, driven by rising energy and food import costs within the EU. Tourism and financial services demand increase service prices, while wage growth adds pressure. Eurozone monetary tightening and stable governance help keep inflation low, though import reliance sustains moderate price increases.