The Egypt economy is driven by tourism, Suez Canal revenues, and agriculture. Historical sites and Red Sea resorts attract visitors, while the canal is a global trade artery. Natural gas exports and remittances are significant, but high population growth, unemployment, and debt pose challenges. Reforms to reduce subsidies and attract investment have spurred growth, though inflation and poverty persist. Infrastructure projects, like the New Administrative Capital, aim to modernize the economy.
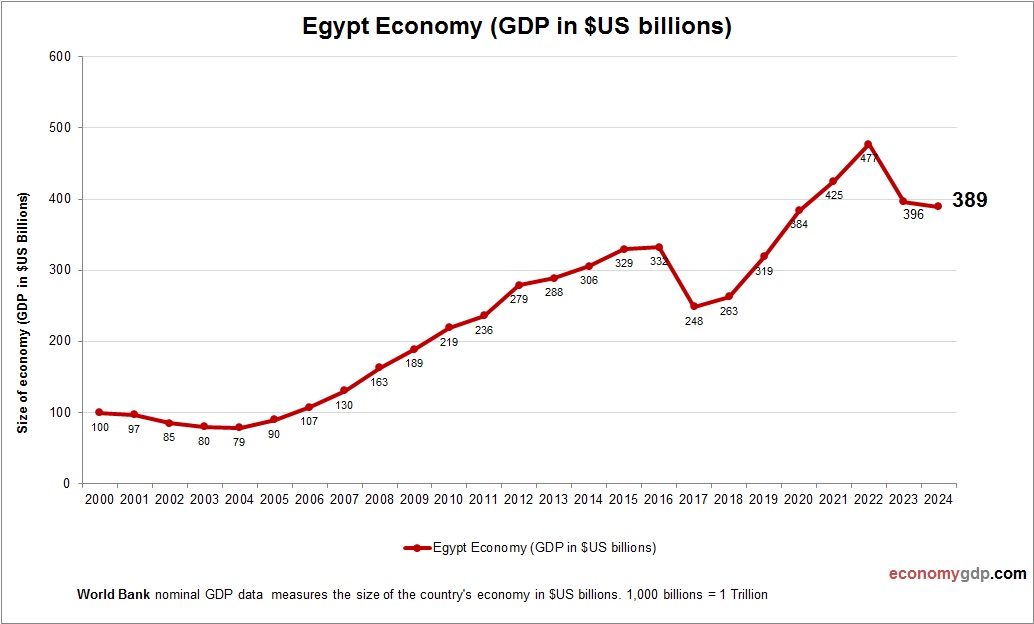
Egypt Economy Size
Egypt’s economy, at $400 billion, is among Africa’s largest. Services, agriculture, and industry fuel its GDP, with growth supported by reforms and population size. See Egypt GDP.
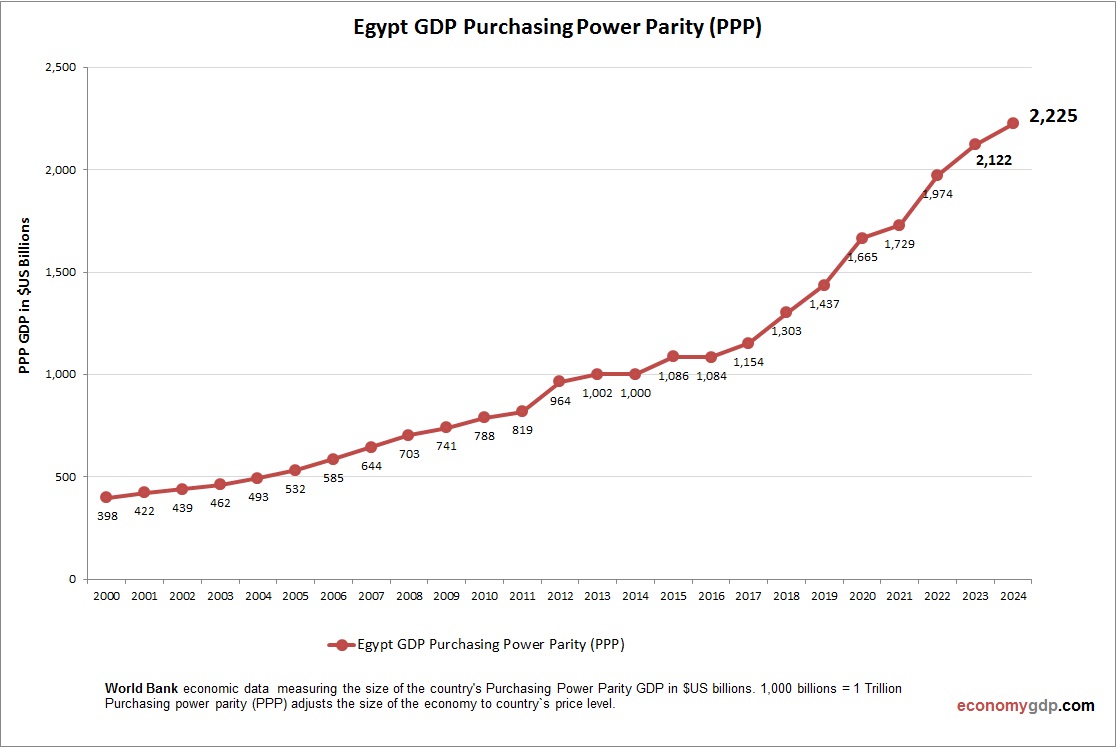
Egypt Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Egypt’s economy has a PPP GDP of $1.8 trillion, over four times its $400 billion nominal GDP, due to low costs for services and agriculture. PPP per capita is about $17,000, indicating modest purchasing power. Large population and domestic pricing amplify market size, but inequality and unemployment constrain PPP-driven gains.
Egypt Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 5.5% in 2024, propelled by agriculture and remittances. Suez Canal revenues and gas exports support growth, but inflation and debt pose risks. Construction and tourism contribute, while economic reforms and foreign investment drive resilience, positioning the economy for robust expansion in the region.

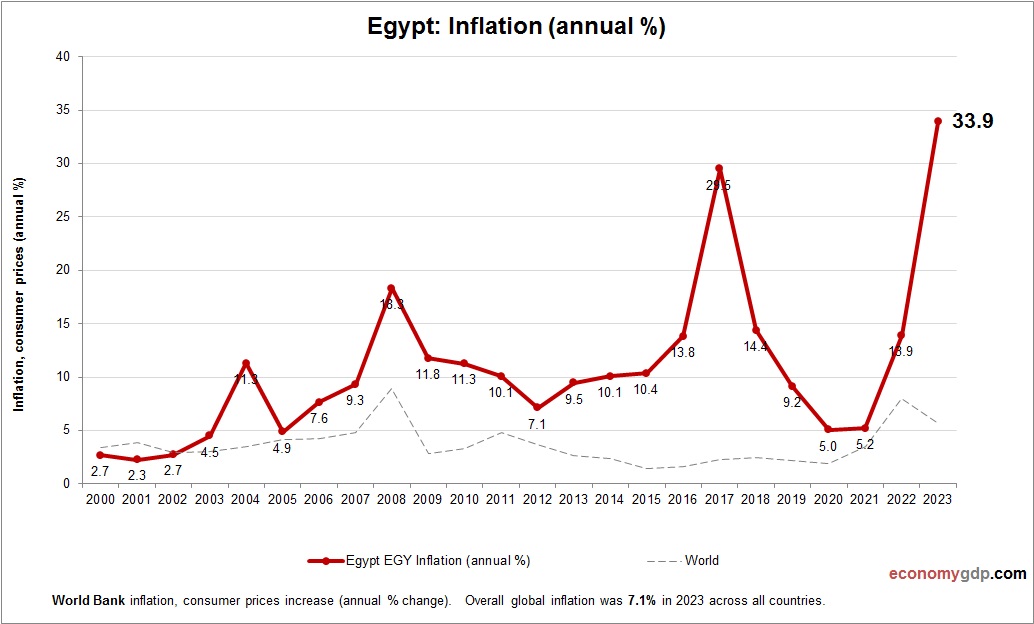
Egypt Inflation
Egypt’s inflation rate is around 25% in 2024, driven by currency depreciation and rising global food and energy prices. Suez Canal disruptions and import reliance increase costs, while fiscal deficits fuel demand. Agricultural setbacks add pressure. Monetary tightening and IMF support aim to stabilize, but high inflation persists in this populous economy.