The Netherlands economy excels in agriculture, logistics, and technology. It’s a global leader in high-tech agriculture, exporting flowers and vegetables. Rotterdam’s port drives logistics and trade. Technology, particularly semiconductors (ASML), is a top industry. Emerging sectors include green hydrogen and AI-driven agriculture. The Netherlands strategic location and infrastructure make it a European trade hub. Its focus on sustainability, with extensive wind energy and circular economy initiatives, supports growth. Despite high costs, its innovative workforce and strong EU ties ensure competitiveness. The digital economy and biotech are also expanding, enhancing its global economic role.
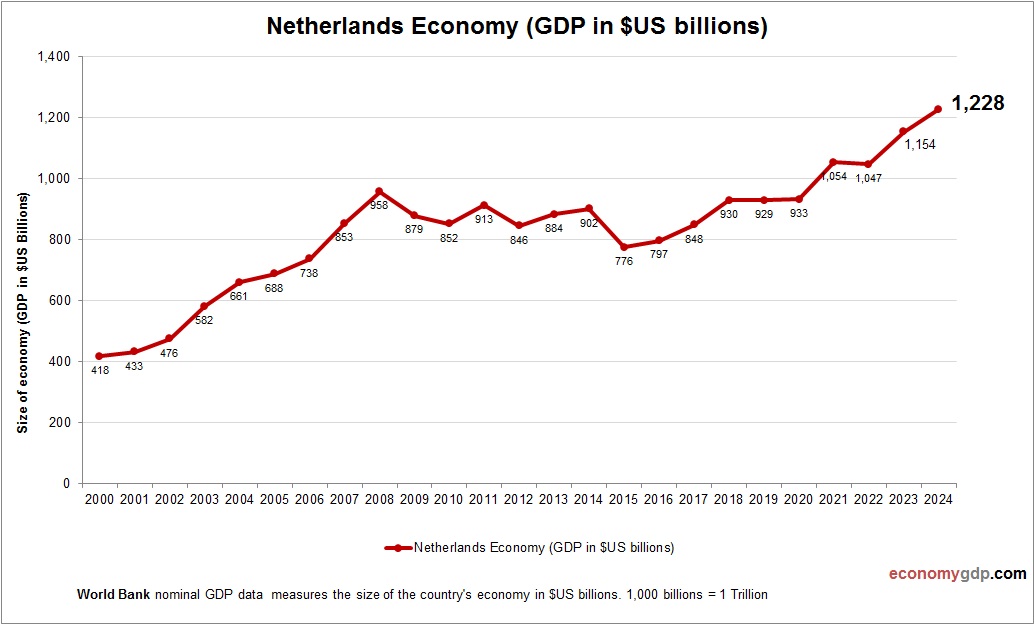
Netherlands Economy Size
The Netherlands economy has a nominal GDP of approximately $1 trillion. Agriculture, logistics, and technology are key drivers, with its port and semiconductor industries prominent. Its GDP reflects a highly open, trade-oriented economy within the EU. Investments in green hydrogen and AI support growth, positioning the Netherlands as a compact but influential economic hub in Europe, with a strong focus on sustainability and innovation. See Netherlands GDP.

Netherlands Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
The Netherlands economy has a PPP GDP of about $1.3 trillion. Agriculture, logistics, and technology drive its size, with PPP reflecting high living costs. Its role as a trade hub and semiconductor leader boosts purchasing power. Investments in green hydrogen and AI enhance its PPP GDP, positioning the Netherlands as a compact but influential EU economy with strong trade and innovation contributions.

Netherlands Growth Rate
The Netherlands economy is forecasted to grow at 1.4% in 2025. Agriculture, logistics, and technology drive expansion, with Rotterdam’s port and ASML’s semiconductors as key assets. EU trade and investments in green hydrogen support growth, though high labor costs pose challenges. The Netherlands open, trade-oriented economy ensures steady progress, reinforcing its role as a European hub for innovation and commerce.

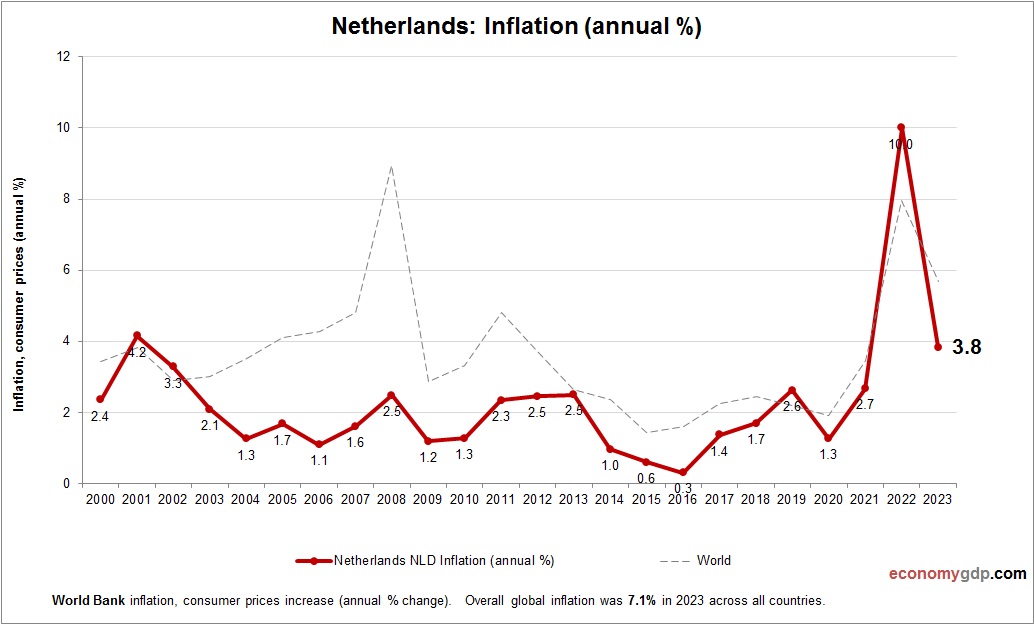
Netherlands Inflation
The Netherlands inflation is low at 1.9%, driven by energy costs and trade reliance. Stable agricultural output and EU integration curb price growth, while high living costs add minor pressure. Investments in green hydrogen and semiconductors help control costs, and tight monetary policy ensures low inflation. The Netherlands open economy maintains price stability despite global trade slowdowns.