Slovenia’s economy, valued at $60 billion, is led by industry, including automotive and pharmaceuticals, with exports driving 80% of GDP. Services, particularly tourism, leverage Alpine and coastal attractions. Agriculture, producing wine and dairy, is small but high-quality. Emerging sectors include green tech, with leadership in sustainable manufacturing, and IT. EU membership ensures trade stability, but an aging population challenges growth. Investments in renewables and innovation position Slovenia as a model for small, export-driven economies, with strong potential in niche markets.
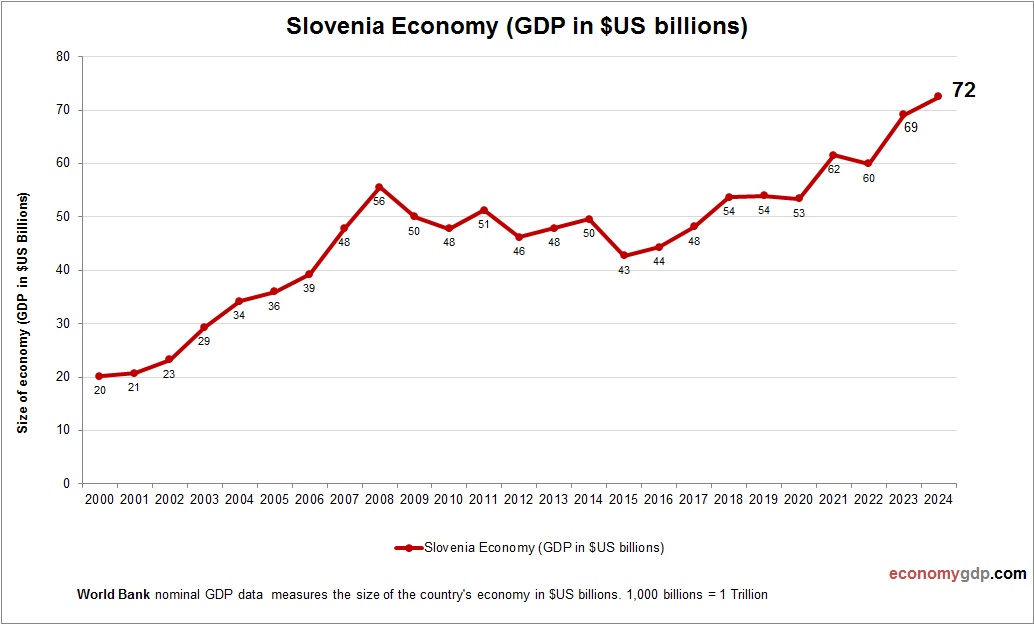
Slovenia Economy Size
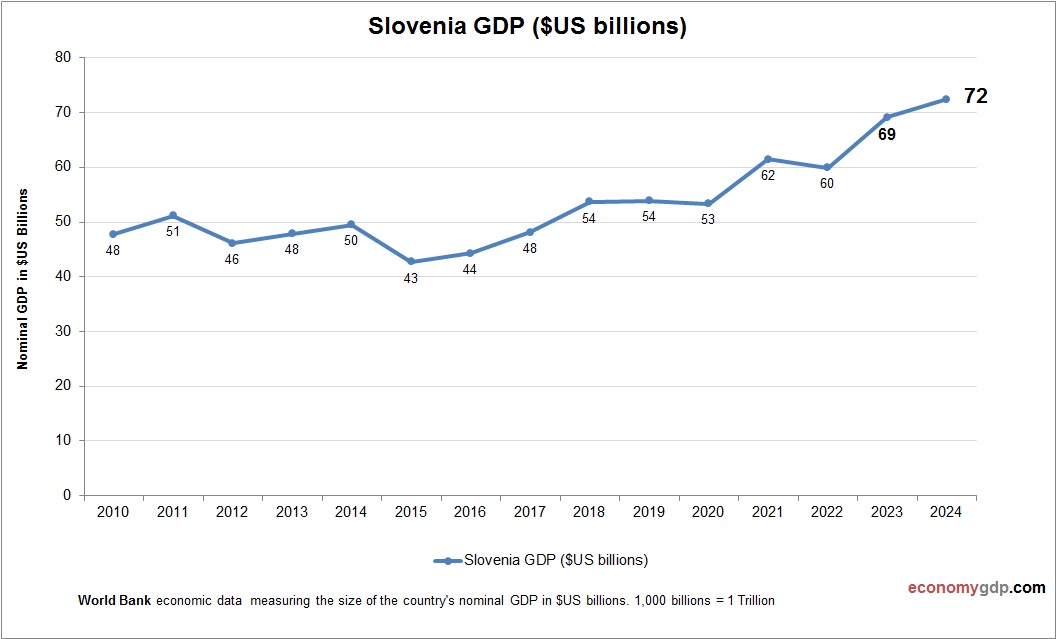
Slovenia’s economy, at $60 billion, is small within the EU, with industry and services driving its GDP, supported by exports. See Slovenia GDP.
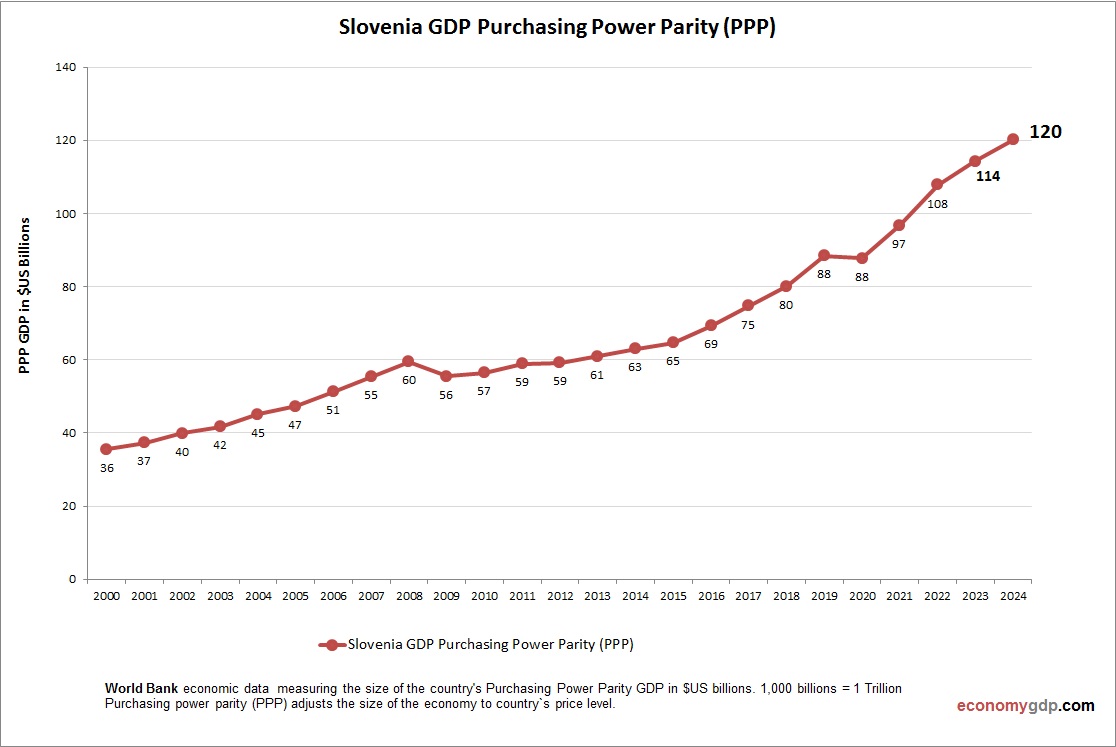
Slovenia Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Slovenia’s economy has a PPP GDP of $110 billion, nearly double its $60 billion nominal GDP, reflecting lower costs for industry and services. PPP per capita is around $55,000, indicating strong purchasing power. Domestic pricing and exports boost markets, supporting robust PPP-driven growth in this small economy.
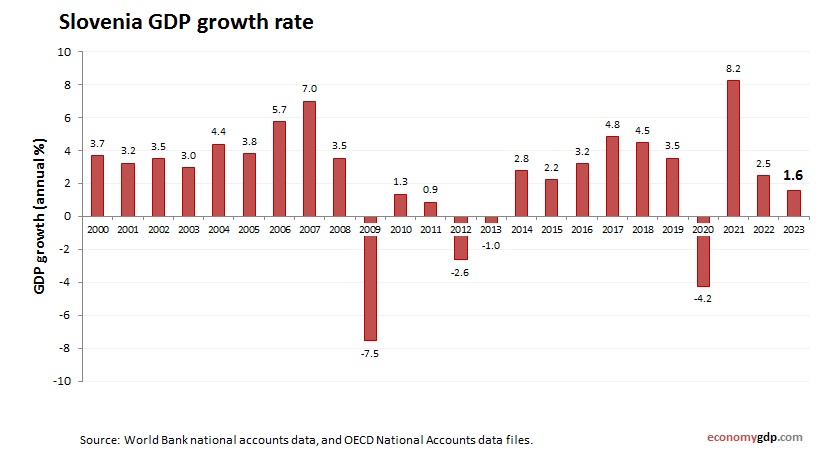
Slovenia Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 2.5% in 2024, fueled by manufacturing and tourism. EU integration and pharmaceutical exports support growth, but an aging population and export reliance limit gains. Green tech contributes, while infrastructure investments drive resilience, positioning the small economy for steady progress.
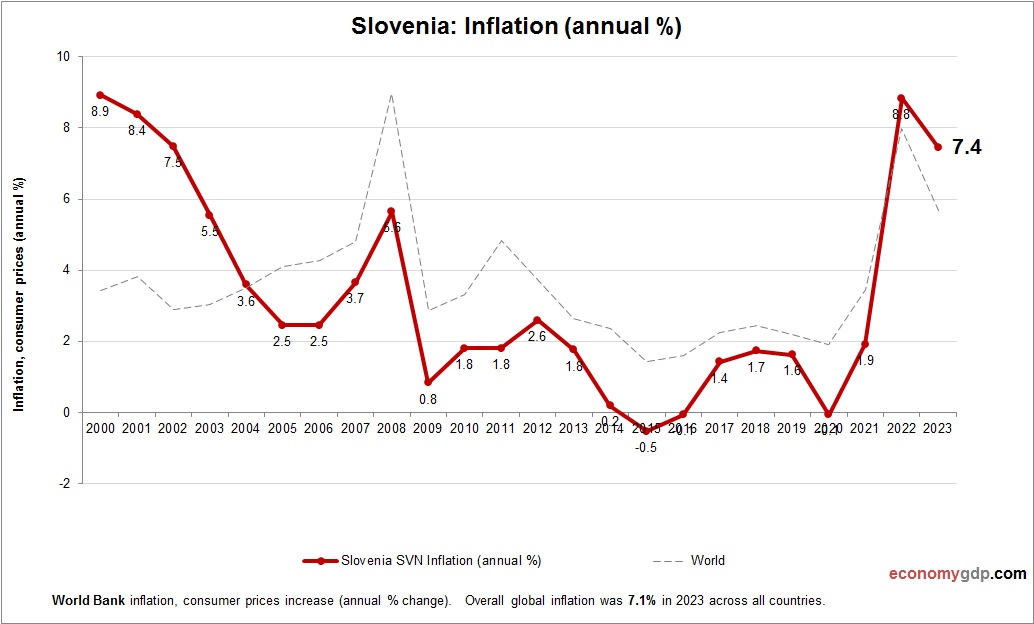
Slovenia Inflation
Slovenia’s inflation rate is around 2.5% in 2024, driven by rising energy and food import costs within the EU. Strong manufacturing exports and tourism demand increase prices, while wage growth adds pressure. Eurozone monetary tightening and stable governance help keep inflation low, though import reliance sustains moderate price increases.