Poland’s economy relies on manufacturing, agriculture, and services. It produces automotive parts, machinery, and electronics, with strong exports to the EU. Agriculture includes grains and pork, while services, particularly logistics, thrive due to Poland’s central location. Emerging industries include IT, with Warsaw’s growing tech hub, and renewable energy, focusing on wind and solar. Poland’s young workforce and EU membership drive growth, though energy transition challenges remain. Investments in green tech and digitalization, alongside a robust manufacturing base, position Poland as an emerging economic power in Eastern Europe, with strong trade and innovation potential.
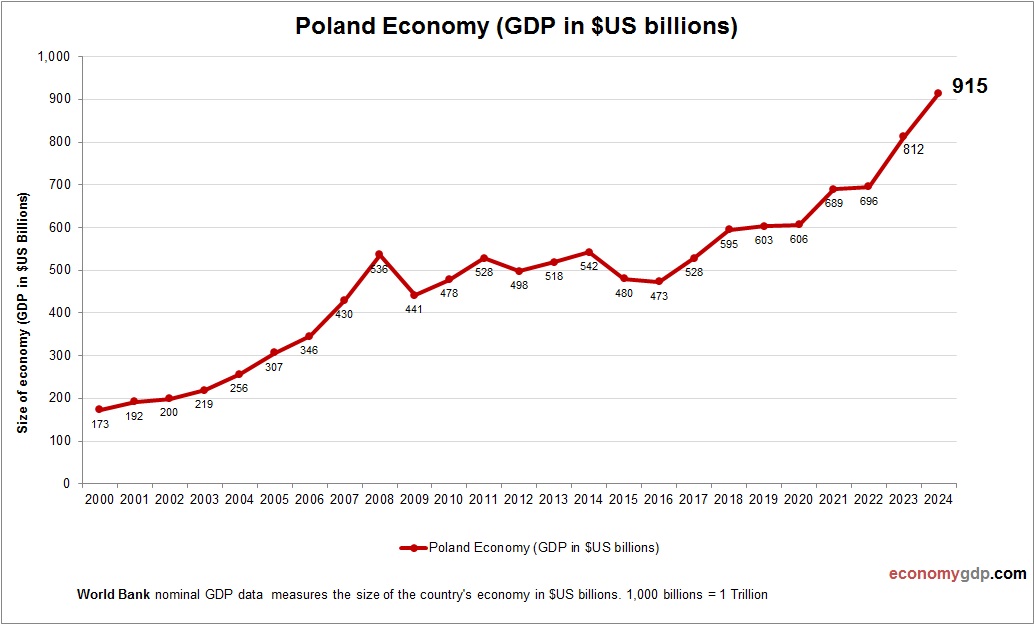
Poland Economy Size
Poland’s economy, with a nominal GDP of about $700 billion, is a rising EU player. Manufacturing, agriculture, and services drive its size, with strong automotive and IT sectors. Its GDP benefits from EU integration and a skilled workforce. Investments in renewable energy and tech hubs support growth, positioning Poland as an emerging economic force in Eastern Europe with significant potential in manufacturing and digital innovation. See Poland GDP.

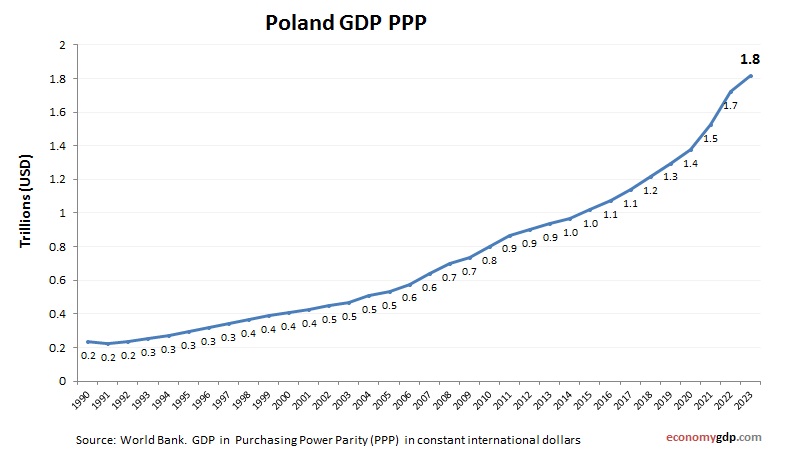
Poland Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Poland’s economy has a PPP GDP of around $1.7 trillion. Manufacturing, agriculture, and services drive its size, with low costs boosting purchasing power. EU integration and automotive exports enhance its PPP GDP, supporting rapid growth. Investments in IT and renewable energy amplify its economic scale, positioning Poland as an emerging Eastern European economy with strong manufacturing and trade contributions.
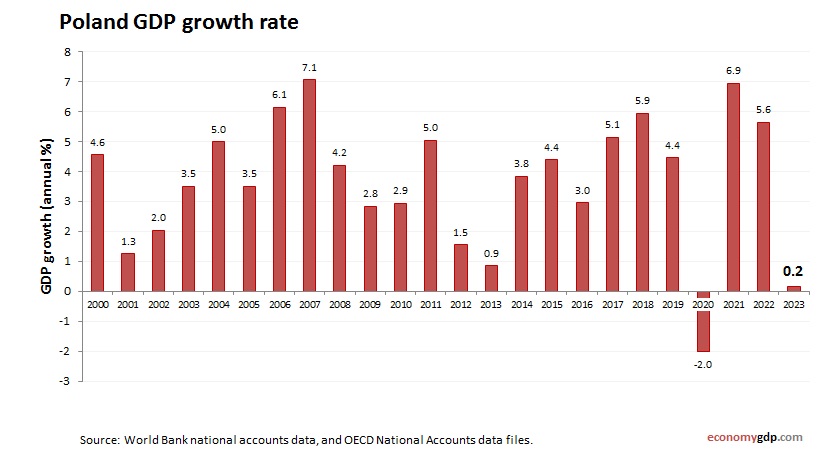
Poland Growth Rate
Poland’s economy is projected to grow at 2.7% in 2025. Manufacturing, agriculture, and services drive expansion, with automotive and IT sectors thriving due to EU integration. Investments in renewable energy and tech hubs like Warsaw support growth, though energy transition costs pose challenges. Poland’s young workforce and trade ties ensure strong growth, positioning it as an emerging economic force in Eastern Europe.
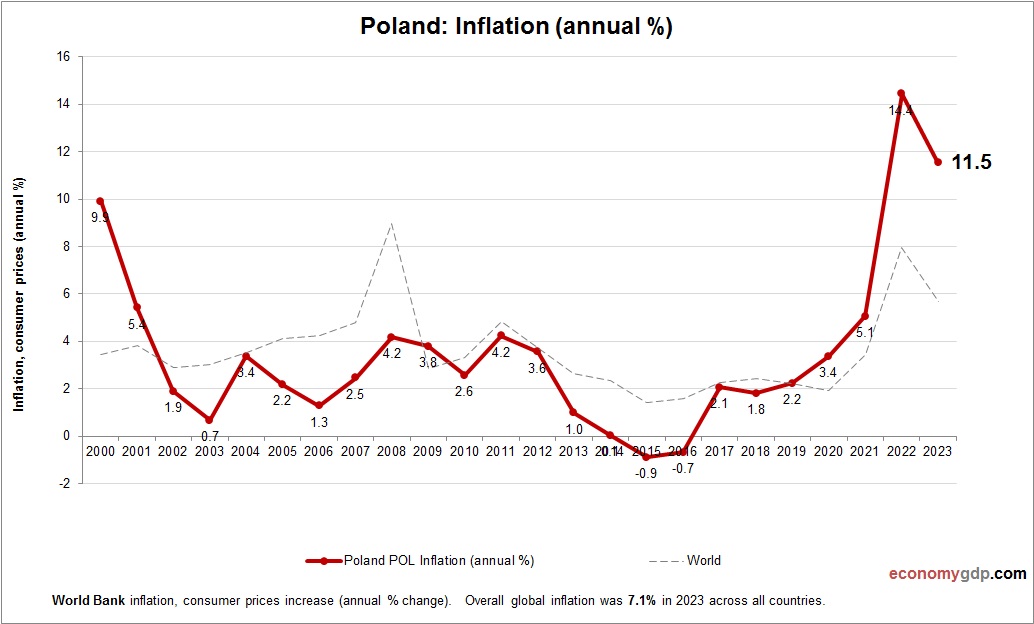
Poland Inflation
The Poland’s inflation is moderate at 3.5%, driven by energy costs and strong domestic demand. EU integration and manufacturing growth add pressure, while food price volatility contributes. Tight monetary policy and stable commodity markets help control inflation, though wage growth sustains increases. Investments in IT and renewables mitigate risks, keeping inflation manageable amid robust economic growth.