The Lebanon economy faces severe challenges due to political instability, debt, and currency collapse. Services, including banking and tourism, were historically strong, but recent crises have crippled these sectors. Remittances and agriculture provide some support, though hyperinflation and unemployment are rampant. Reconstruction and reform efforts are stalled by corruption and regional tensions. Recovery hinges on international aid and governance improvements, with limited prospects for short-term stabilization.
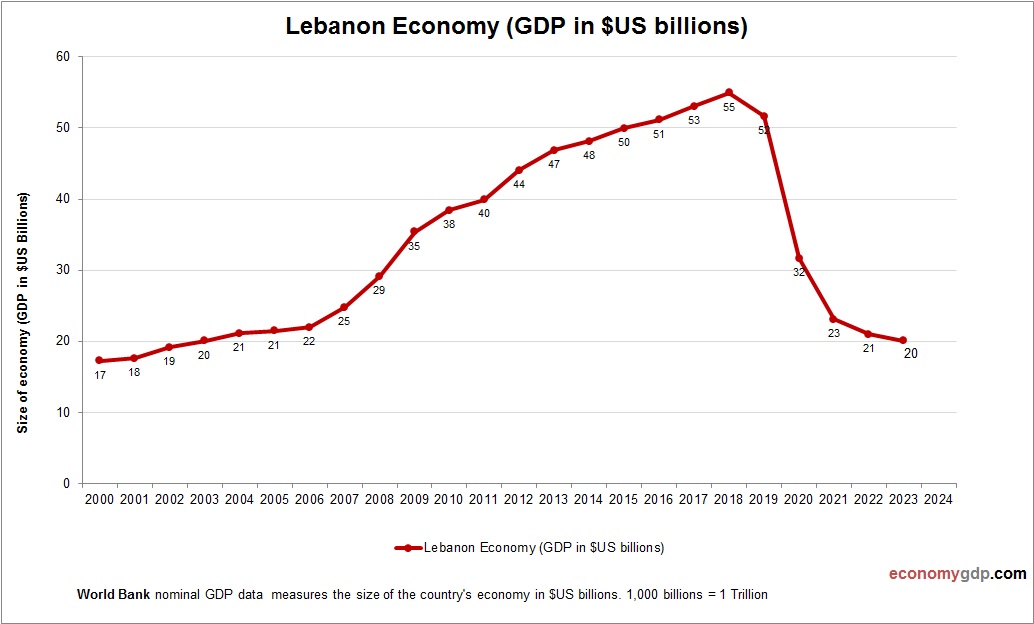
Lebanon Economy Size
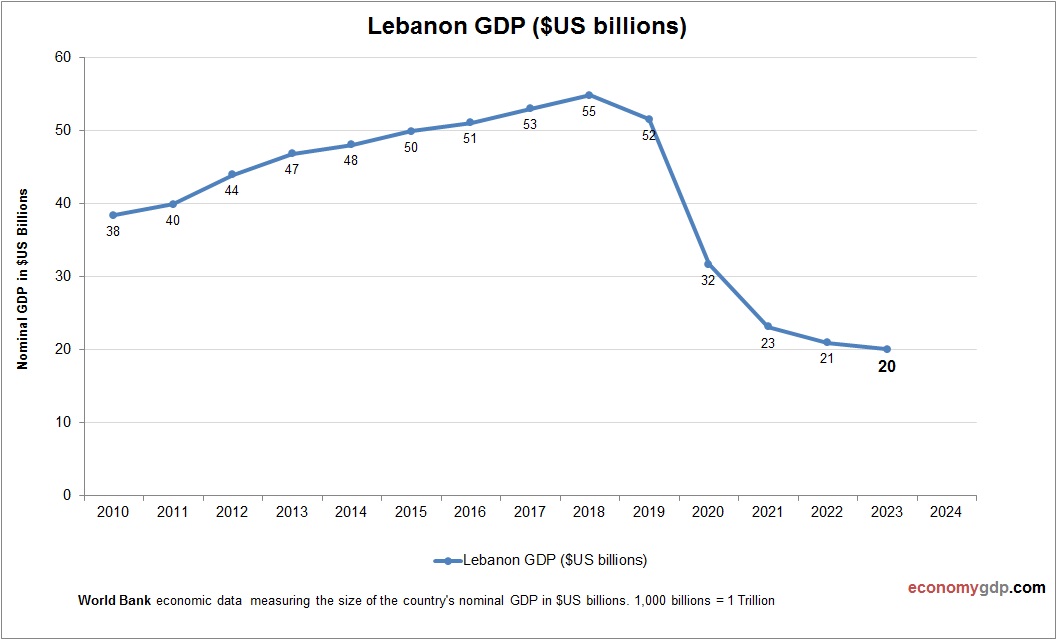
Lebanon’s economy, at $20 billion, is small and contracting, with services and remittances shaping its GDP, crippled by debt and political crises. See Lebanon GDP.
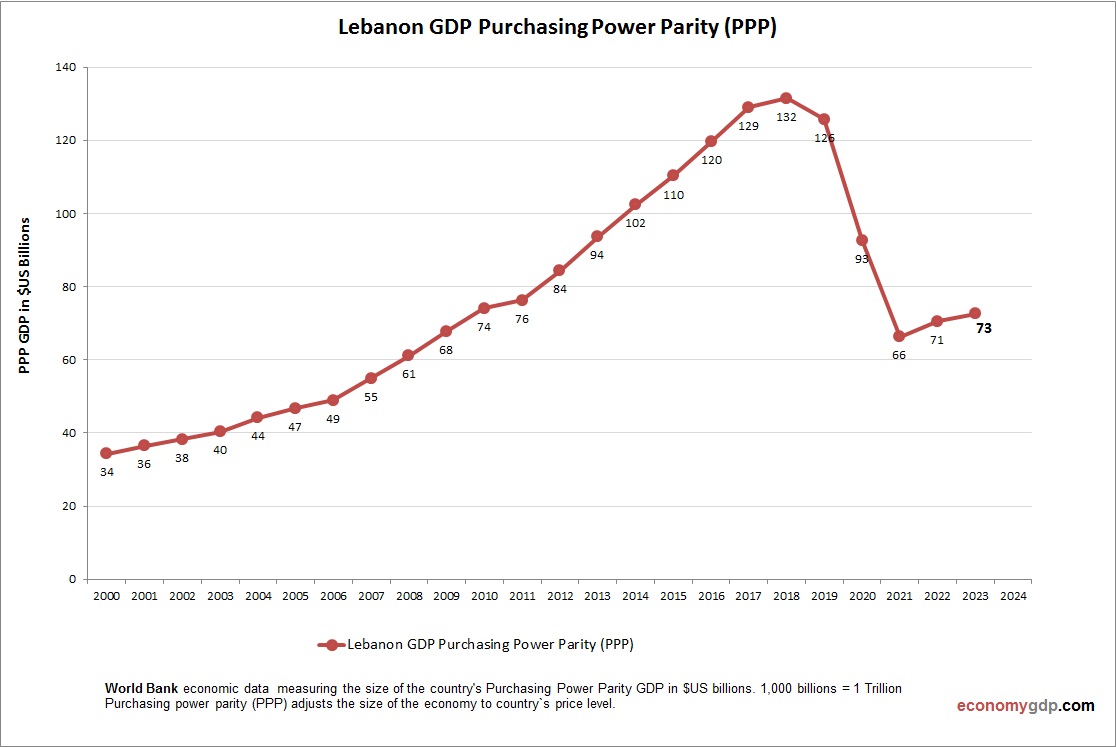
Lebanon Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Lebanon’s economy has a PPP GDP of $80 billion, four times its $20 billion nominal GDP, due to low costs for services and remittances. PPP per capita is around $14,000, reflecting modest purchasing power. Debt and political crises limit PPP benefits, though domestic pricing supports local markets.
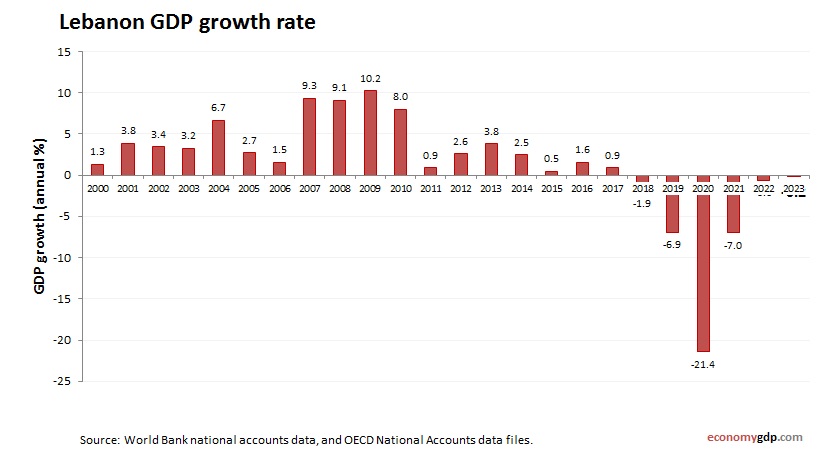
Lebanon Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is -2.0% in 2024, reflecting contraction due to debt and political crises. Remittances and informal trade drive limited activity, but banking collapse and inflation hinder progress. Tourism and agriculture contribute minimally, while international aid supports resilience, though recovery remains elusive without structural reforms.
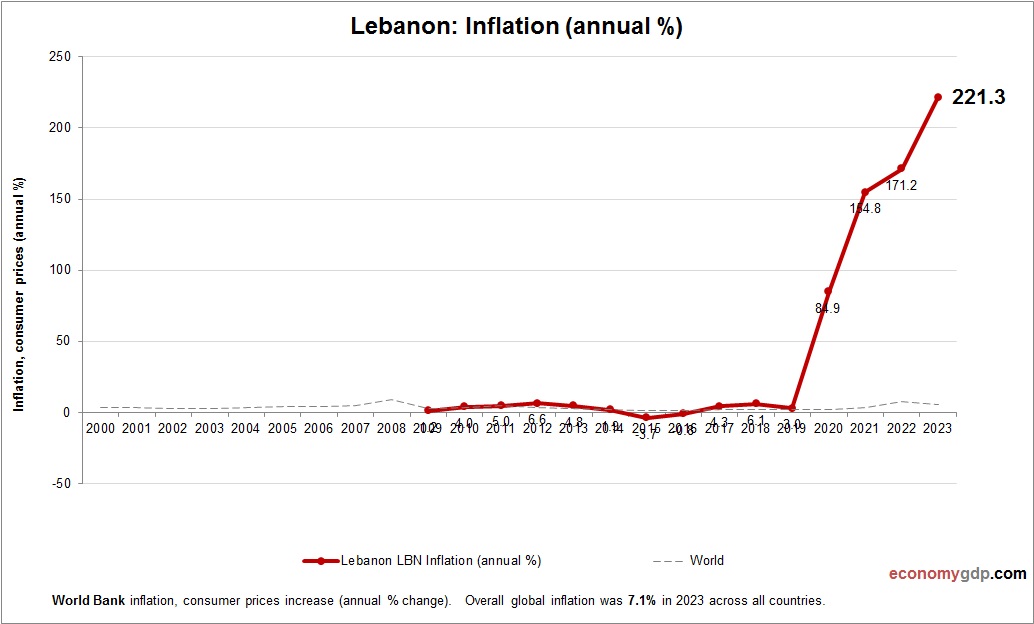
Lebanon Inflation
Lebanon’s inflation rate is around 70% in 2024, among the highest globally, driven by currency collapse and banking crisis. Import reliance for food and fuel skyrockets costs, while political instability disrupts supply chains. Remittances provide some relief, but fiscal mismanagement and lack of reforms sustain hyperinflation, severely impacting living standards.