The Iran economy is heavily oil-dependent, with petroleum driving exports. Agriculture, including pistachios and saffron, and manufacturing also contribute. Sanctions have constrained growth, causing inflation and unemployment spikes. A large domestic market and skilled workforce offer potential, but political isolation and mismanagement hinder progress. Efforts to diversify into petrochemicals and technology face challenges, with black-market trade and regional tensions shaping economic prospects.
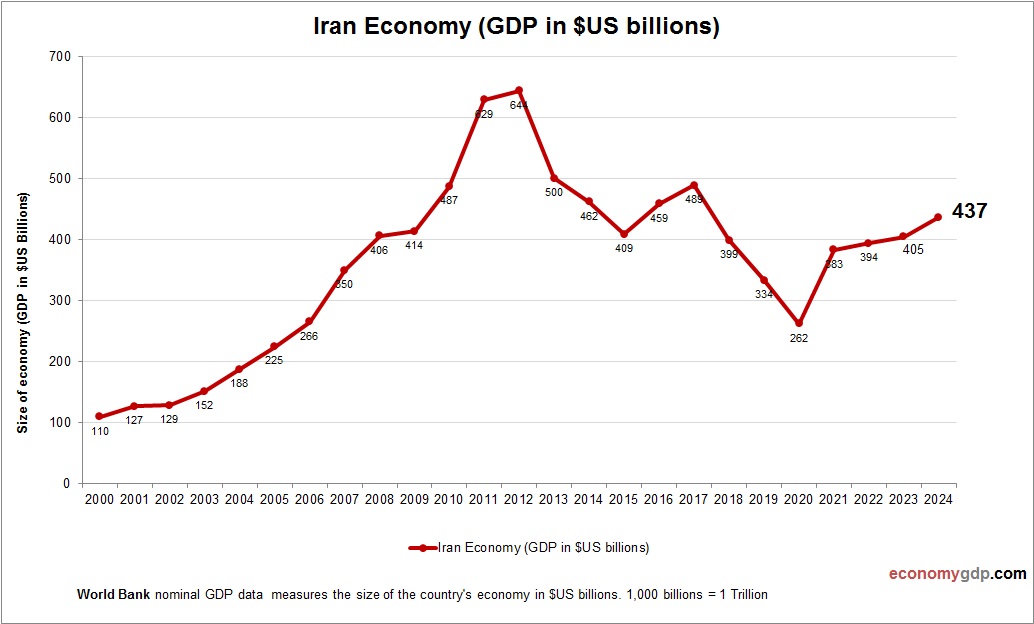
Iran Economy Size
Iran’s economy, at $200 billion, is large but constrained by sanctions, with oil and industry driving its GDP despite economic isolation challenges. See Iran GDP.
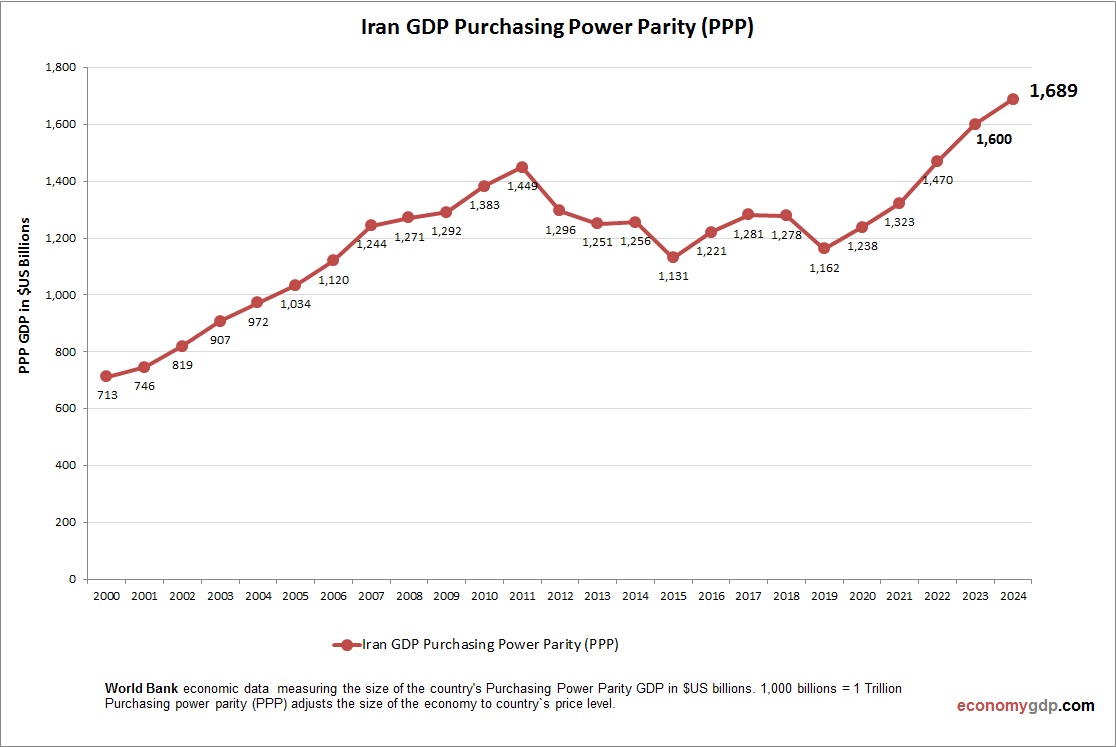
Iran Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Iran’s economy has a PPP GDP of $1.7 trillion, over eight times its $200 billion nominal GDP, due to low local costs for oil and industry. PPP per capita is around $20,000, reflecting moderate purchasing power. Sanctions limit trade, but PPP highlights a large domestic market with potential for growth if restrictions ease.
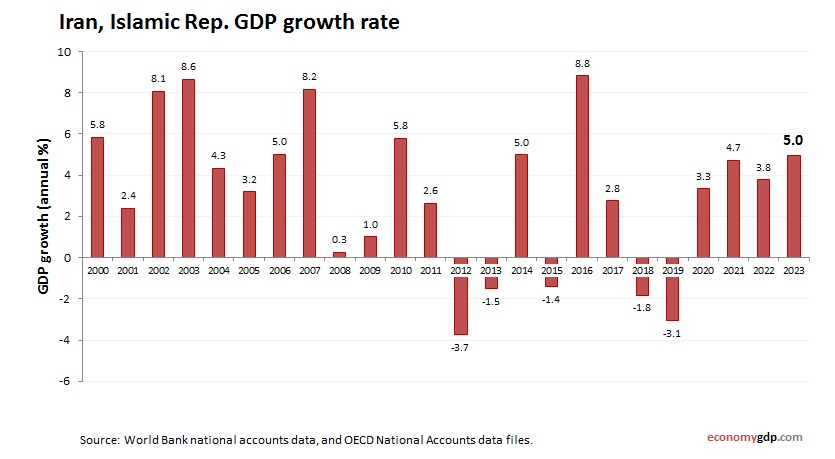
Iran Growth Rate
The economic growth rate is 3.5% in 2024, driven by oil exports despite sanctions. Agriculture and manufacturing contribute modestly, but inflation and restricted trade limit gains. Informal markets and domestic production drive resilience, while currency stabilization efforts support growth, positioning the economy for moderate progress amidst isolation.
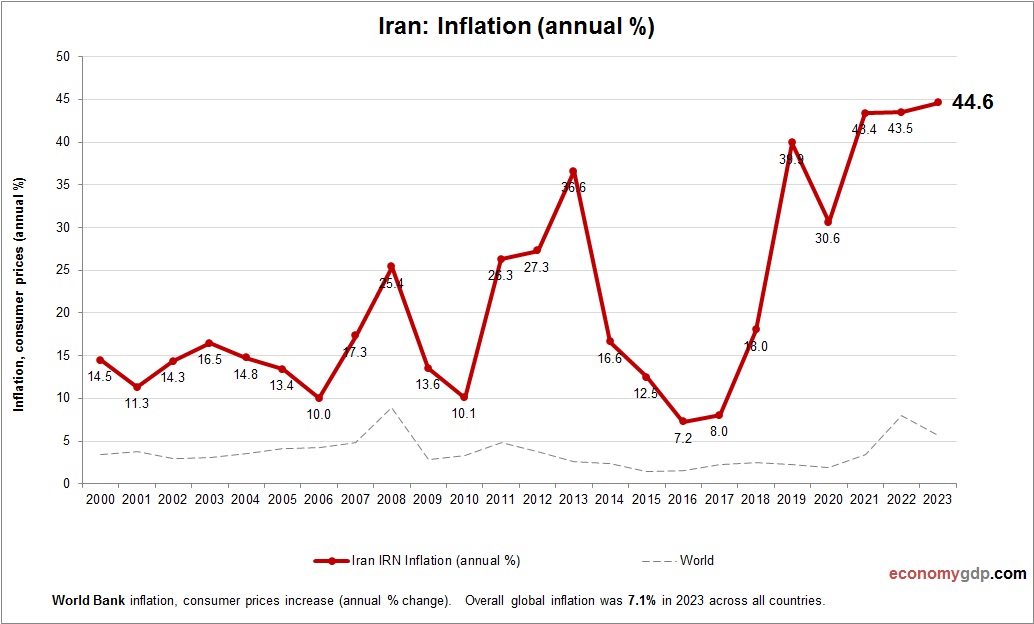
Iran Inflation
Iran’s inflation rate is about 35% in 2024, among the highest globally, driven by sanctions and currency depreciation. Import restrictions increase food and fuel costs, while fiscal deficits fuel demand. Oil exports drive some demand, but limited trade access and monetary expansion sustain high inflation, impacting living standards.