Spain’s economy relies on tourism, agriculture, and automotive industries. It’s a top global tourism destination, with Barcelona and Madrid drawing millions. Agriculture, including olives, wine, and citrus, is a major export sector. Automotive manufacturing, led by firms like SEAT, is significant. Emerging industries include renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, and smart tourism technologies. Spain’s Mediterranean climate supports agribusiness, while its EU membership drives trade. Challenges like unemployment persist, but investments in green tech and digital infrastructure, alongside cultural heritage, strengthen Spain’s economy and its role in Europe’s sustainable future.
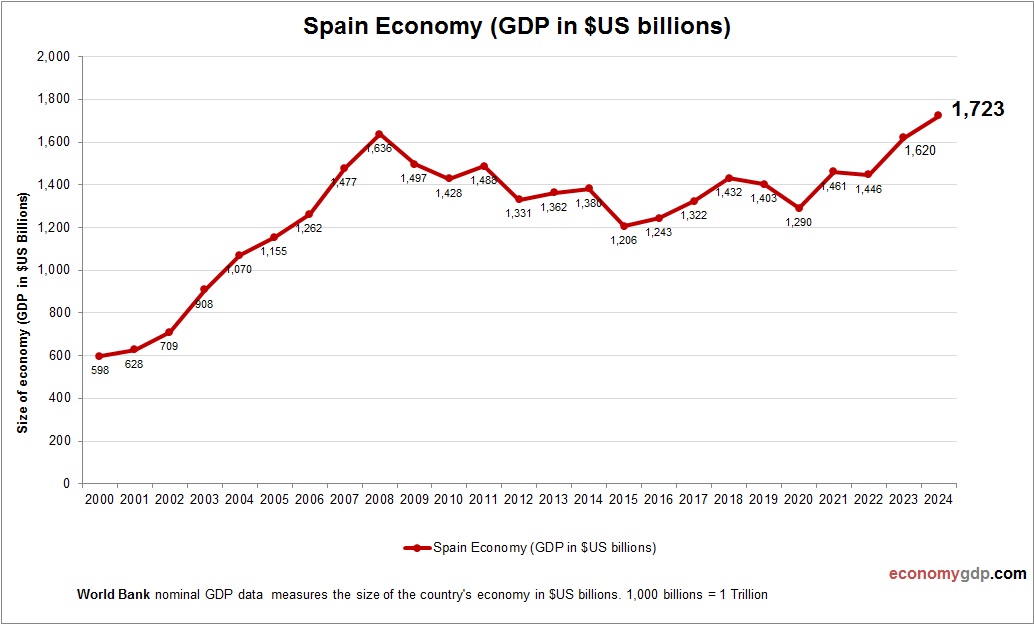
Spain Economy Size
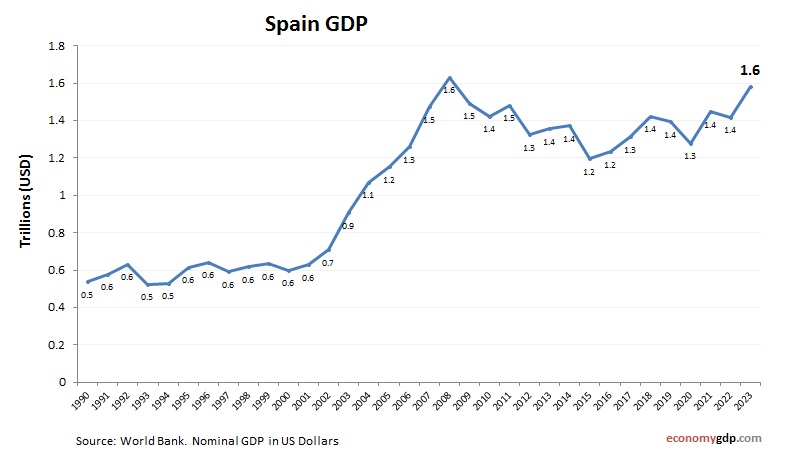
Spain’s economy, with a nominal GDP of about $1.4 trillion, is a major EU player. Tourism, agriculture, and automotive industries drive its size, with strong exports to Europe. Its GDP reflects a recovery from past economic challenges, supported by EU integration and infrastructure investments. Growth in renewable energy and digital tourism enhances its economic scale, positioning Spain as a key contributor to the European economy. See Spain GDP.
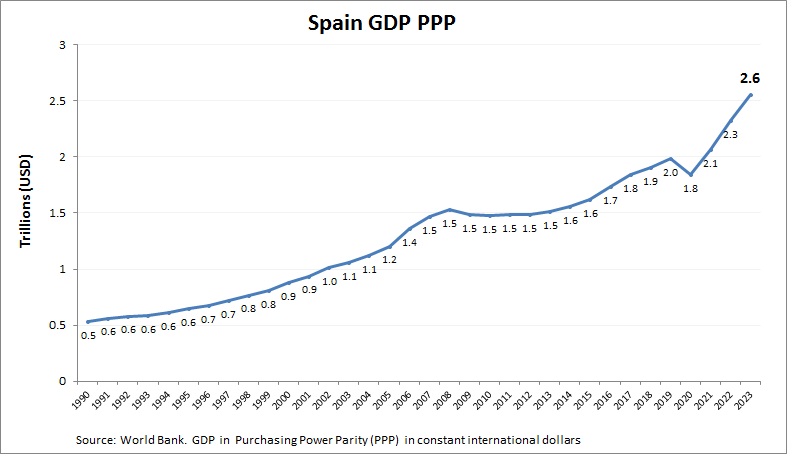
Spain Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Spain’s economy has a PPP GDP of around $2.1 trillion. Tourism, agriculture, and automotive industries drive its size, with PPP reflecting lower living costs. EU trade and infrastructure investments boost purchasing power, supporting a robust economy. Growth in renewable energy and digital tourism enhances its PPP GDP, positioning Spain as a key EU economy with strong contributions to tourism and manufacturing.
Spain Growth Rate
Spain’s economy is expected to grow at 1.9% in 2025. Tourism, agriculture, and automotive industries drive expansion, with EU trade providing stability. Investments in renewable energy and smart tourism technologies boost growth, though unemployment remains a concern. Spain’s recovery from past economic challenges and strong cultural appeal ensure moderate growth, positioning it as a key contributor to the EU’s economic output.

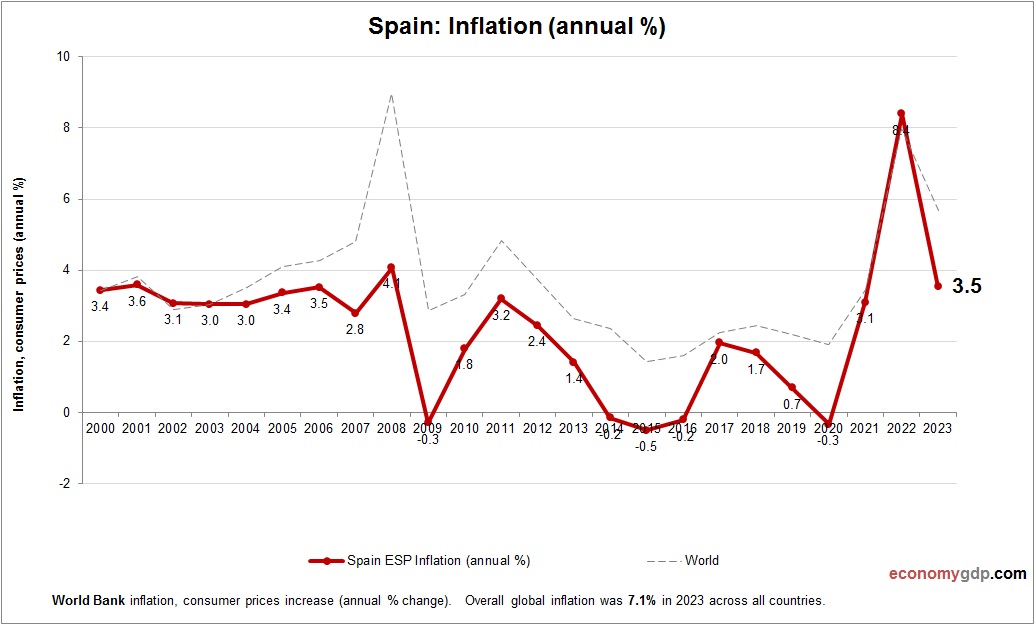
Spain Inflation
The Spain’s inflation is low at 2%, driven by energy costs and tourism recovery. EU trade and stable food prices curb price growth, while high unemployment limits consumer demand. Investments in renewable energy and digital tourism help control costs, though import reliance adds minor pressure. Tight monetary policy ensures inflation remains low, supporting Spain’s economic recovery and stability.