India’s economy is diverse, with services, particularly IT and software, leading globally, driven by firms like Infosys and TCS. Agriculture remains a backbone, employing millions in rice, wheat, and textile production. Manufacturing, including pharmaceuticals and textiles, is a top industry, with India as a generic drug hub. Emerging sectors include AI, fintech, and biotechnology, with startups thriving in Bangalore. Renewable energy, especially solar, is expanding rapidly. India’s young workforce and digital infrastructure fuel growth, though challenges like rural poverty persist. Its focus on innovation and global outsourcing solidifies its role as an emerging economic giant.
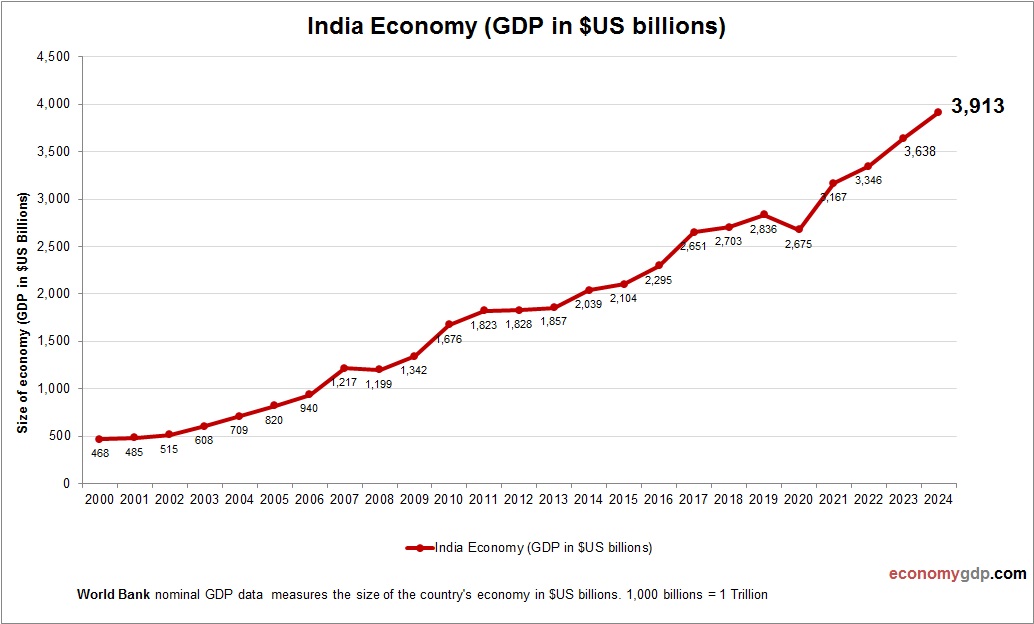
India Economy Size
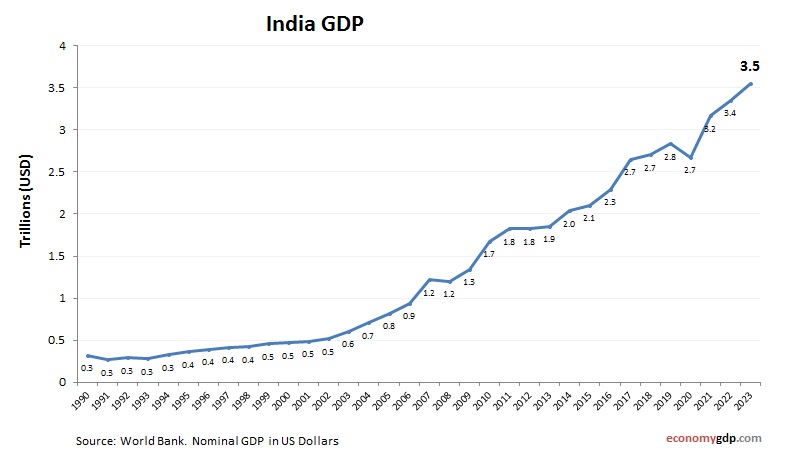
India’s economy, the fifth largest, has a nominal GDP of around $3.9 trillion. Services, particularly IT, and agriculture drive growth, with a burgeoning manufacturing sector. Its young population and digital economy fuel rapid expansion, positioning India as an emerging global powerhouse. Despite infrastructure challenges, economic reforms and foreign investment bolster its GDP, with India’s growth trajectory suggesting it could soon overtake larger economies, driven by tech and consumer markets. See India GDP.
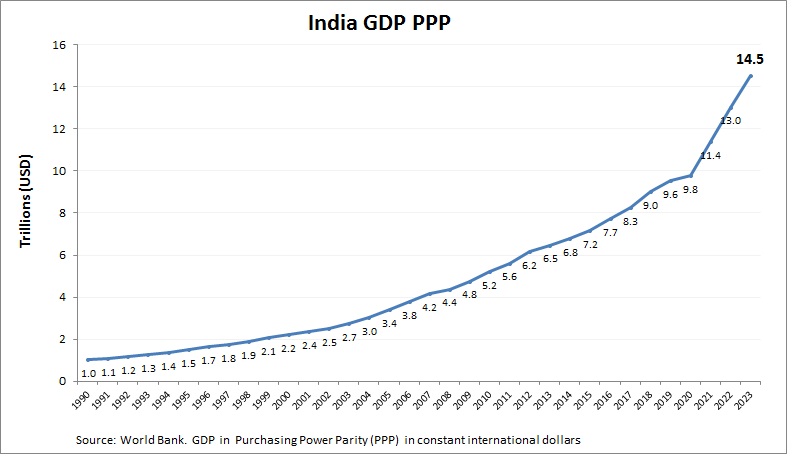
India Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
India’s economy, with a PPP GDP of about $14 trillion, is a global leader. Services, agriculture, and manufacturing fuel its size, with low costs boosting purchasing power. India’s young population and digital economy drive rapid growth, making its PPP GDP one of the largest. Investments in IT and renewable energy enhance its economic scale, positioning India as an emerging powerhouse with significant domestic consumption and global influence.
India Growth Rate
India’s economy, the fastest-growing major economy, is projected to expand by 6.2% in 2025. IT services, manufacturing, and agriculture drive growth, fueled by a young workforce and digitalization. Infrastructure investments and renewable energy projects boost momentum. Despite rural poverty challenges, robust domestic demand and reforms position India for strong growth, enhancing its global economic influence and attracting foreign investment.

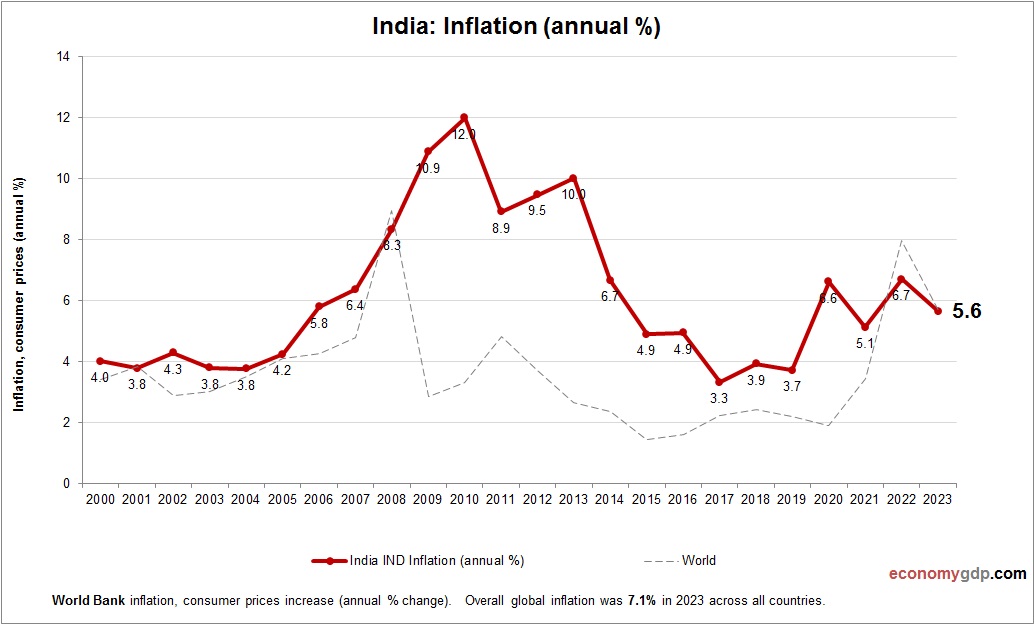
India Inflation
The India’s inflation is moderate at 4.5%, driven by food and energy price volatility. Strong domestic demand and infrastructure spending contribute, while monsoon-dependent agriculture impacts food costs. Tight monetary policy and improved supply chains help control inflation, but urban consumption and fuel import reliance sustain price pressures. Reforms and digital growth mitigate some risks, keeping inflation within a manageable range.