The Gambia's GDP is small but relies on agriculture, remittances, and tourism. Groundnuts are a primary export crop, alongside rice, millet, and fish. Tourism contributes significantly, drawing visitors to beaches, culture, and wildlife. Remittances from Gambians abroad play a vital role in supporting households. Services, including trade and transport, are growing in importance. However, limited infrastructure, poverty, and vulnerability to external shocks constrain growth. Efforts are ongoing to diversify into renewable energy, horticulture, and small-scale manufacturing. Despite its size, The Gambia's youthful population and geographic location offer opportunities for gradual economic development and regional trade integration.
World Bank GDP economic data: 2010-2024. Last updated Oct 2025.
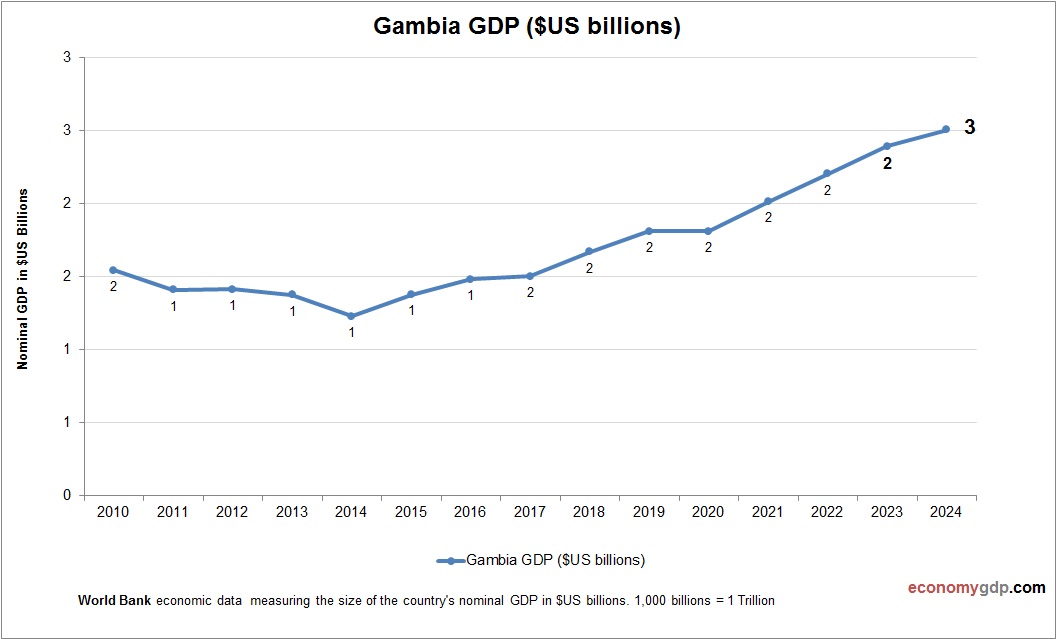
Gambia GDP Statistics by Year
| Year | GDP Size (in billions $) |
| 2025 (projected) | 3 |
| 2024 | 3 |
| 2023 | 2 |
| 2022 | 2 |
| 2021 | 2 |
| 2020 | 2 |
| 2019 | 2 |
| 2018 | 2 |
| 2017 | 2 |
| 2016 | 1 |
| 2015 | 1 |
| 2014 | 1 |
| 2013 | 1 |
| 2012 | 1 |
| 2011 | 1 |
| 2010 | 2 |
