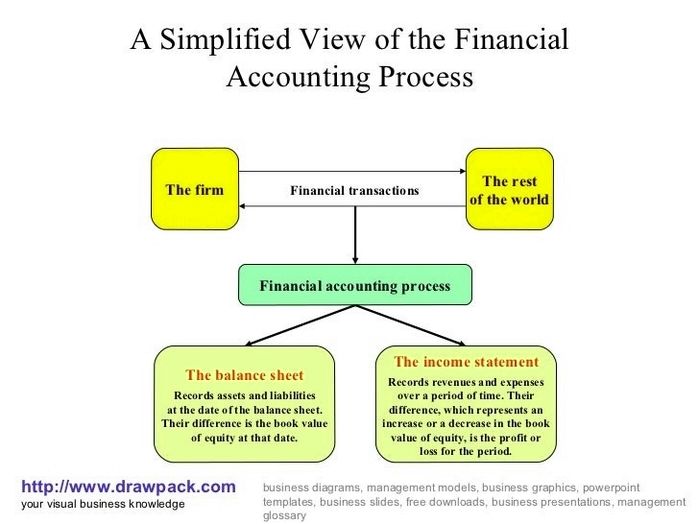
The accounting cycle is the holistic process of recording and processing all financial transactions of a company. It involves a series of steps that ensure accurate and reliable financial reporting. Here are the eight steps in the accounting cycle:
1. Transactions: Financial transactions are identified and recorded.
2. Journal Entries: Transactions are recorded in a journal.
3. Posting: Journal entries are posted to the general ledger.
4. Unadjusted Trial Balance: An unadjusted trial balance is prepared to ensure debits equal credits.
5. Worksheet: A worksheet is used to make adjusting entries and prepare financial statements.
6. Adjusting Journal Entries: Adjusting entries are made to correct errors or allocate revenues and expenses.
7. Financial Statements: Financial statements, including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, are prepared.
8. Closing the Books: Temporary accounts are closed, and the results are transferred to permanent accounts.
The accounting cycle ensures that financial transactions are accurately recorded, summarized, and reported in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). It provides a systematic approach to maintain accurate financial records and produce reliable financial statements for decision-making purposes.
Please note that this is a general overview of the accounting cycle, and each step may involve more detailed processes depending on the complexity of the transactions and reporting requirements.
