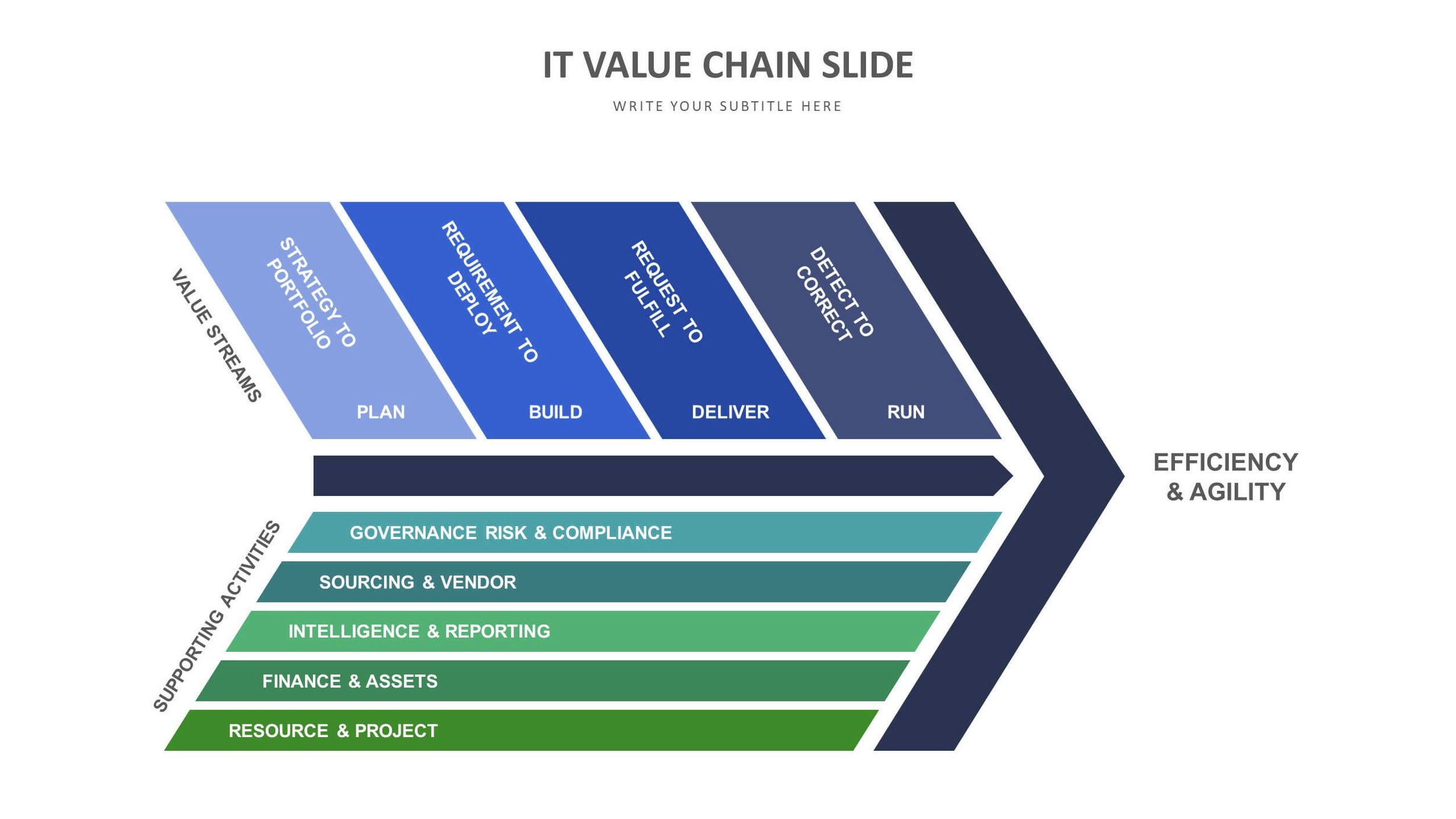
A value chain is a series of consecutive steps that go into the creation of a finished product, from its initial design to its arrival at a customer’s door. The chain identifies each step in the process at which value is added, including the sourcing, manufacturing, and marketing stages of its production. A company conducts a value-chain analysis by evaluating the detailed procedures involved in each step of its business. The purpose of a value-chain analysis is to increase production efficiency so that a company can deliver maximum value for the least possible cost .
The value chain theory analyzes a firm’s five primary activities and four support activities. The primary activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. The support activities include procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure. The goal of a value chain is to create a competitive advantage for a company by increasing productivity while keeping costs reasonable .
Michael E. Porter, of Harvard Business School, introduced the concept of a value chain in his book, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. He wrote: “Competitive advantage cannot be understood by looking at a firm as a whole. It stems from the many discrete activities a firm performs in designing, producing, marketing, delivering, and supporting its product.” In other words, it’s important to maximize value at each specific point in a firm’s processes .
